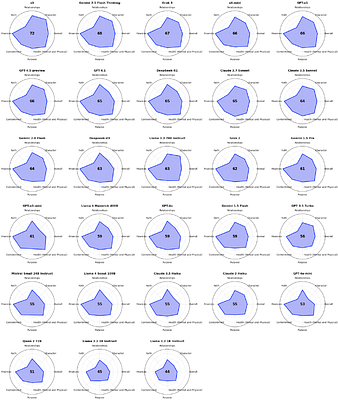
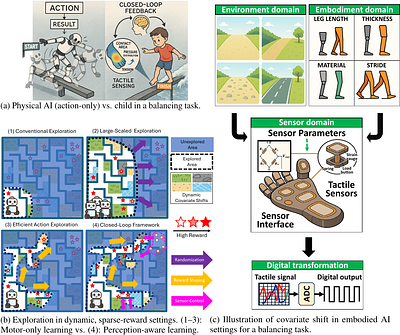
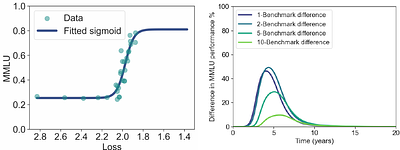
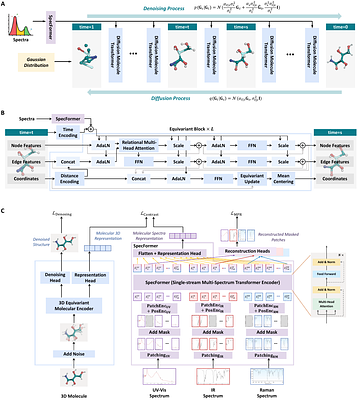
Stable Preference Optimization for LLMs: A Bilevel Approach Beyond Direct Preference Optimization
By: Chengtao Jian, Kai Yang, Ye Ouyang, Xiaozhou Ye
By: Sukjun Hwang, Brandon Wang, Albert Gu
By: Perry Dong, Qiyang Li, Dorsa Sadigh, Chelsea Finn
By: Ziyue Li, Yang Li, Tianyi Zhou
By: Elizabeth Hilliard, Akshaya Jagadeesh, Alex Cook, Steele Billings, Nicholas Skytland, Alicia Llewellyn, Jackson Paull, Nathan Paull, Nolan Kurylo, Keatra Nesbitt, Robert Gruenewald, Anthony Jantzi, Omar Chavez
By: Eunsu Baek, Keondo Park, Jeonggil Ko, Min-hwan Oh, Taesik Gong, Hyung-Sin Kim
By: Hans Gundlach, Jayson Lynch, Neil Thompson
By: Liang Wang, Yu Rong, Tingyang Xu, Zhenyi Zhong, Zhiyuan Liu, Pengju Wang, Deli Zhao, Qiang Liu, Shu Wu, Liang Wang
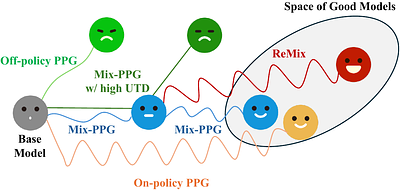
Squeeze the Soaked Sponge: Efficient Off-policy Reinforcement Finetuning for Large Language Model
By: Jing Liang, Hongyao Tang, Yi Ma, Jinyi Liu, Yan Zheng, Shuyue Hu, Lei Bai, Jianye Hao
By: Roberto Pereira, Fernanda Famá, Asal Rangrazi, Marco Miozzo, Charalampos Kalalas, Paolo Dini