By: Zili Meng, Nirav Atre, Mingwei Xu, Justine Sherry, Maria Apostolaki
When many users and unique applications share a congested edge link (e.g., a home network), everyone wants their own application to continue to perform well despite contention over network resources. Traditionally, network engineers have focused on fairness as the key objective to ensure that competing applications are equitably and led by the switch, and hence have deployed fair queueing mechanisms. However, for many network workloads toda... more
When many users and unique applications share a congested edge link (e.g., a home network), everyone wants their own application to continue to perform well despite contention over network resources. Traditionally, network engineers have focused on fairness as the key objective to ensure that competing applications are equitably and led by the switch, and hence have deployed fair queueing mechanisms. However, for many network workloads today, strict fairness is directly at odds with equitable application performance. Real-time streaming applications, such as videoconferencing, suffer the most when network performance is volatile (with delay spikes or sudden and dramatic drops in throughput). Unfortunately, "fair" queueing mechanisms lead to extremely volatile network behavior in the presence of bursty and multi-flow applications such as Web traffic. When a sudden burst of new data arrives, fair queueing algorithms rapidly shift resources away from incumbent flows, leading to severe stalls in real-time applications. In this paper, we present Confucius, the first practical queue management scheme to effectively balance fairness against volatility, providing performance outcomes that benefit all applications sharing the contended link. Confucius outperforms realistic queueing schemes by protecting the real-time streaming flows from stalls in competing with more than 95% of websites. Importantly, Confucius does not assume the collaboration of end-hosts, nor does it require manual parameter tuning to achieve good performance. less
By: Leandro C. de Almeida, Rafael Pasquini, Chrysa Papagianni, Fábio L. Verdi
Routers employ queues to temporarily hold packets when the scheduler cannot immediately process them. Congestion occurs when the arrival rate of packets exceeds the processing capacity, leading to increased queueing delay. Over time, Active Queue Management (AQM) strategies have focused on directly draining packets from queues to alleviate congestion and reduce queuing delay. On Programmable Data Plane (PDP) hardware, AQMs traditionally res... more
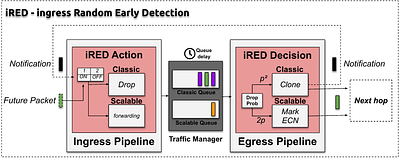
Routers employ queues to temporarily hold packets when the scheduler cannot immediately process them. Congestion occurs when the arrival rate of packets exceeds the processing capacity, leading to increased queueing delay. Over time, Active Queue Management (AQM) strategies have focused on directly draining packets from queues to alleviate congestion and reduce queuing delay. On Programmable Data Plane (PDP) hardware, AQMs traditionally reside in the Egress pipeline due to the availability of queue delay information there. We argue that this approach wastes the router's resources because the dropped packet has already consumed the entire pipeline of the device. In this work, we propose ingress Random Early Detection (iRED), a more efficient approach that addresses the Egress drop problem. iRED is a disaggregated P4-AQM fully implemented in programmable data plane hardware and also supports Low Latency, Low Loss, and Scalable Throughput (L4S) framework, saving device pipeline resources by dropping packets in the Ingress block. To evaluate iRED, we conducted three experiments using a Tofino2 programmable switch: i) An in-depth analysis of state-of-the-art AQMs on PDP hardware, using 12 different network configurations varying in bandwidth, Round-Trip Time (RTT), and Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU). The results demonstrate that iRED can significantly reduce router resource consumption, with up to a 10x reduction in memory usage, 12x fewer processing cycles, and 8x less power consumption for the same traffic load; ii) A performance evaluation regarding the L4S framework. The results prove that iRED achieves fairness in bandwidth usage for different types of traffic (classic and scalable); iii) A comprehensive analysis of the QoS in a real setup of a DASH) technology. iRED demonstrated up to a 2.34x improvement in FPS and a 4.77x increase in the video player buffer fill. less
By: Mohamed Rihan, Tim Due, MohammadAmin Vakilifard, Dirk Wubben, Armin Dekorsy
Leveraging non-terrestrial platforms in 6G networks holds immense significance as it opens up opportunities to expand network coverage, enhance connectivity, and support a wide range of innovative applications, including global-scale Internet of Things and ultra-high-definition content delivery. To accomplish the seamless integration between terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks, substantial changes in radio access network (RAN) architec... more
Leveraging non-terrestrial platforms in 6G networks holds immense significance as it opens up opportunities to expand network coverage, enhance connectivity, and support a wide range of innovative applications, including global-scale Internet of Things and ultra-high-definition content delivery. To accomplish the seamless integration between terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks, substantial changes in radio access network (RAN) architecture are required. These changes involve the development of new RAN solutions that can efficiently manage the diverse characteristics of both terrestrial and non-terrestrial components, ensuring smooth handovers, resource allocation, and quality of service across the integrated network ecosystem. Additionally, the establishment of robust interconnection and communication protocols between terrestrial and non-terrestrial elements will be pivotal to utilize the full potential of 6G technology. Additionally, innovative approaches have been introduced to split the functionalities within the RAN into centralized and distributed domains. These novel paradigms are designed to enhance RAN's flexibility while simultaneously lowering the costs associated with infrastructure deployment, all while ensuring that the quality of service for end-users remains unaffected. In this work, we provide an extensive examination of various Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) architectures and the necessary adaptations required on the existing 5G RAN architecture to align with the distinct attributes of NTN. Of particular significance, we emphasize the crucial RAN functional split choices essential for the seamless integration of terrestrial and non-terrestrial components within advanced 6G networks. less
By: Jan Cychnerski, Bartłomiej Mróz
This paper describes an architecture design process for Networked Music Performance (NMP) platform for medium-sized conducted music ensembles, based on remote rehearsals of Academic Choir of Gdansk University of Technology. The issues of real-time remote communication, in-person music performance, and NMP are described. Three iterative steps defining and extending the architecture of the NMP platform with additional features to enhance its ... more
This paper describes an architecture design process for Networked Music Performance (NMP) platform for medium-sized conducted music ensembles, based on remote rehearsals of Academic Choir of Gdansk University of Technology. The issues of real-time remote communication, in-person music performance, and NMP are described. Three iterative steps defining and extending the architecture of the NMP platform with additional features to enhance its utility in remote rehearsals are presented. The first iteration uses a regular video conferencing platform, the second iteration uses dedicated NMP devices and tools, and the third iteration adds video transmission and utilizes professional low-latency audio and video workstations. For each iteration, the platform architecture is defined and deployed with simultaneous usability tests. Its strengths and weaknesses are identified through qualitative and quantitative measurements - statistical analysis shows a significant improvement in rehearsal quality after each iteration. The final optimal architecture is described and concluded with guidelines for creating NMP systems for said music ensembles. less
By: Marc Mosko
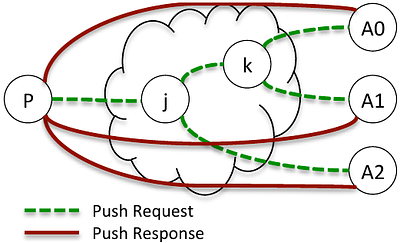
We describe a method to achieve distributed consensus in a Content Centric Network using the PAXOS algorithm. Consensus is necessary, for example, if multiple writers wish to agree on the current version number of a CCNx name or if multiple distributed systems wish to elect a leader for fast transaction processing. We describe two forms of protocols, one using standard CCNx Interest request and Content Object response, and the second using ... more
We describe a method to achieve distributed consensus in a Content Centric Network using the PAXOS algorithm. Consensus is necessary, for example, if multiple writers wish to agree on the current version number of a CCNx name or if multiple distributed systems wish to elect a leader for fast transaction processing. We describe two forms of protocols, one using standard CCNx Interest request and Content Object response, and the second using a CCNx Push request and response. We further divide the protocols in to those using the CCNx 0.x protocol where Content Object name may continue Interest names and the CCNx 1.0 protocol where Content Object names exactly match Interest names. less
By: Arun Kumar Silivery, Ram Mohan Rao Kovvur
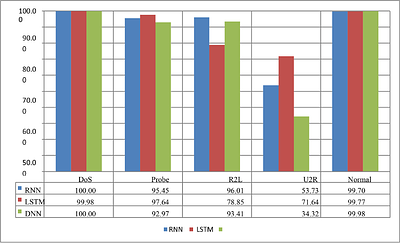
This proposed model introduces novel deep learning methodologies. The objective here is to create a reliable intrusion detection mechanism to help identify malicious attacks. Deep learning based solution framework is developed consisting of three approaches. The first approach is Long-Short Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network (LSTM-RNN) with seven optimizer functions such as adamax, SGD, adagrad, adam, RMSprop, nadam and adadelta. The mode... more
This proposed model introduces novel deep learning methodologies. The objective here is to create a reliable intrusion detection mechanism to help identify malicious attacks. Deep learning based solution framework is developed consisting of three approaches. The first approach is Long-Short Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network (LSTM-RNN) with seven optimizer functions such as adamax, SGD, adagrad, adam, RMSprop, nadam and adadelta. The model is evaluated on NSL-KDD dataset and classified multi attack classification. The model has outperformed with adamax optimizer in terms of accuracy, detection rate and low false alarm rate. The results of LSTM-RNN with adamax optimizer is compared with existing shallow machine and deep learning models in terms of accuracy, detection rate and low false alarm rate. The multi model methodology consisting of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), Long-Short Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network (LSTM-RNN), and Deep Neural Network (DNN). The multi models are evaluated on bench mark datasets such as KDD99, NSL-KDD, and UNSWNB15 datasets. The models self-learnt the features and classifies the attack classes as multi-attack classification. The models RNN, and LSTM-RNN provide considerable performance compared to other existing methods on KDD99 and NSL-KDD dataset less
By: Guocong Quan, Atilla Eryilmaz, Ness Shroff
The ever-growing end user data demands, and the simultaneous reductions in memory costs are fueling edge-caching deployments. Caching at the edge is substantially different from that at the core and needs to take into account the nature of individual data demands. For example, an individual user may not be interested in requesting the same data item again, if it has recently requested it. Such individual dynamics are not apparent in the agg... more
The ever-growing end user data demands, and the simultaneous reductions in memory costs are fueling edge-caching deployments. Caching at the edge is substantially different from that at the core and needs to take into account the nature of individual data demands. For example, an individual user may not be interested in requesting the same data item again, if it has recently requested it. Such individual dynamics are not apparent in the aggregated data requests at the core and have not been considered in popularity-driven caching designs for the core. Hence, these traditional caching policies could induce significant inefficiencies when applied at the edges. To address this issue, we develop new edge caching policies optimized for the individual demands that also leverage overhearing opportunities at the wireless edge. With the objective of maximizing the hit ratio, the proposed policies will actively evict the data items that are not likely to be requested in the near future, and strategically bring them back into the cache through overhearing when they are likely to be popular again. Both theoretical analysis and numerical simulations demonstrate that the proposed edge caching policies could outperform the popularity-driven policies that are optimal at the core. less
By: Claudio Fiandrino, Leonardo Bonati, Salvatore D'Oro, Michele Polese, Tommaso Melodia, Joerg Widmer
The Open Radio Access Network (RAN) paradigm is transforming cellular networks into a system of disaggregated, virtualized, and software-based components. These self-optimize the network through programmable, closed-loop control, leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) routines. In this context, Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has shown great potential in addressing complex resource allocation problems. However, ... more
The Open Radio Access Network (RAN) paradigm is transforming cellular networks into a system of disaggregated, virtualized, and software-based components. These self-optimize the network through programmable, closed-loop control, leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) routines. In this context, Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has shown great potential in addressing complex resource allocation problems. However, DRL -based solutions are inherently hard to explain, which hinders their deployment and use in practice. In this paper, we propose EXPLORA, a framework that provides explainability of DRL-based control solutions for the Open RAN ecosystem. EXPLORA synthesizes network-oriented explanations based on an attributed graph that produces a link between the actions taken by a DRL agent (i.e., the nodes of the graph) and the input state space (i.e., the attributes of each node). This novel approach allows EXPLORA to explain models by providing information on the wireless context in which the DRL agent operates. EXPLORA is also designed to be lightweight for real-time operation. We prototype EXPLORA and test it experimentally on an O-RAN-compliant near-real-time RIC deployed on the Colosseum wireless network emulator. We evaluate EXPLORA for agents trained for different purposes and showcase how it generates clear network-oriented explanations. We also show how explanations can be used to perform informative and targeted intent-based action steering and achieve median transmission bitrate improvements of 4% and tail improvements of 10%. less
By: Xianzhi Zhang, Linchang Xiao, Yipeng Zhou, Miao Hu, Di Wu, Gang Liu
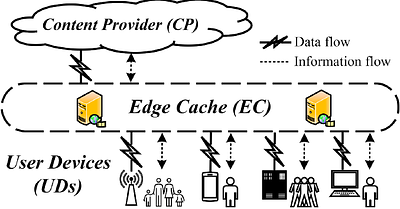
As users conveniently stream their favored online videos, video request records will be automatically seized by video content providers, which may leak users' privacy. Unfortunately, most existing privacy-enhancing approaches are not applicable for protecting users' privacy in requests, which cannot be easily altered or distorted by users and must be visible for content providers to stream correct videos. To preserve request privacy in onli... more
As users conveniently stream their favored online videos, video request records will be automatically seized by video content providers, which may leak users' privacy. Unfortunately, most existing privacy-enhancing approaches are not applicable for protecting users' privacy in requests, which cannot be easily altered or distorted by users and must be visible for content providers to stream correct videos. To preserve request privacy in online video services, it is possible to request additional videos irrelevant to users' interests so that content providers cannot precisely infer users' interest information. However, a naive redundant requesting approach will significantly degrade the performance of edge caches and increase bandwidth overhead accordingly. In this paper, we are among the first to propose a Cache-Friendly Redundant Video Requesting (cRVR) algorithm for User Devices (UDs) and its corresponding caching algorithm for the Edge Cache (EC), which can effectively mitigate the problem of request privacy leakage with minimal impact on the EC's performance. To solve the problem, we develop a Stackelberg game to analyze the dedicated interaction between UDs and EC and obtain their optimal strategies to maximize their respective utility. For UDs, the utility function is a combination of both video playback utility and privacy protection utility. We theoretically prove the existence and uniqueness of the equilibrium of the Stackelberg game. In the end, extensive experiments are conducted with real traces to demonstrate that cRVR can effectively protect video request privacy by reducing up to 57.96\% of privacy disclosure compared to baseline algorithms. Meanwhile, the caching performance of ECs is only slightly affected. less
By: Tra Huong Thi Le, Yan Kyaw Tun
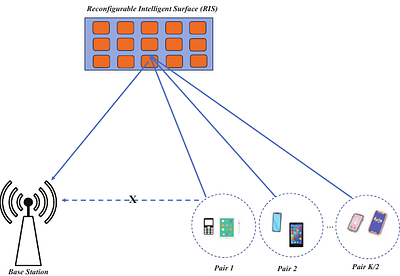
One of the primary objectives for future wireless communication networks is to facilitate the provision of ultra-reliable and low-latency communication services while simultaneously ensuring the capability for vast connection. In order to achieve this objective, we examine a hybrid multi-access scheme inside the finite blocklength (FBL) regime. This system combines the benefits of non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and time-division mult... more
One of the primary objectives for future wireless communication networks is to facilitate the provision of ultra-reliable and low-latency communication services while simultaneously ensuring the capability for vast connection. In order to achieve this objective, we examine a hybrid multi-access scheme inside the finite blocklength (FBL) regime. This system combines the benefits of non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and time-division multiple access (TDMA) schemes with the aim of fulfilling the objectives of future wireless communication networks. In addition, a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is utilized to facilitate the establishment of the uplink transmission between the base station and mobile devices in situations when impediments impede their direct communication linkages. This paper aims to minimize the worst-case decoding-error probability for all mobile users by jointly optimizing power allocation, receiving beamforming, blocklength, RIS reflection, and user pairing. To deal with the coupled variables in the formulated mixed-integer non-convex optimization problem, we decompose it into three sub-problems, namely, 1) decoding order determination problem, 2) joint power allocation, receiving beamforming, RIS reflection, and blocklength optimization problem, and 3) optimal user pairing problem. Then, we provide the sequential convex approximation (SCA) and semidefinite relaxation (SDR)-based algorithms as potential solutions for iteratively addressing the deconstructed first two sub-problems at a fixed random user pairing. In addition, the Hungarian matching approach is employed to address the challenge of optimizing user pairing. In conclusion, we undertake a comprehensive simulation, which reveals the advantageous qualities of the proposed algorithm and its superior performance compared to existing benchmark methods. less