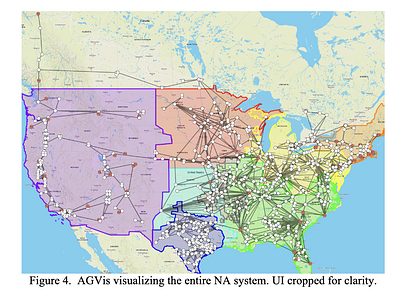
By: Nicholas Parsly, Jinning Wang, Nick West, Qiwei Zhang, Hantao Cui, Fangxing Li
This paper introduces the messaging environment and the geographical
visualization tool of the CURENT Large-scale Testbed (LTB) that can be used for
large-scale power system closed-loop simulation. First, Distributed Messaging
Environment (DiME) implements an asynchronous shared workspace to enable
high-concurrent data exchange. Second, Another Grid Visualizer (AGVis) is
presented as a geovisualization tool that facilitates the visualizatio... more
This paper introduces the messaging environment and the geographical
visualization tool of the CURENT Large-scale Testbed (LTB) that can be used for
large-scale power system closed-loop simulation. First, Distributed Messaging
Environment (DiME) implements an asynchronous shared workspace to enable
high-concurrent data exchange. Second, Another Grid Visualizer (AGVis) is
presented as a geovisualization tool that facilitates the visualization of
real-time power system simulation. Third, case studies show the use of DiME and
AGVis. The results demonstrate that, with the modular structure, the LTB is
capable of not only federal use for real-time, large-scale power system
simulation, but also independent use for customized power system research.
less
By: Ji-An Pan, Qing Xu, Keqiang Li, Chunying Yang, Jianqiang Wang
This article is devoted to addressing the cloud control of connected
vehicles, specifically focusing on analyzing the effect of bi-directional
communication-induced delays. To mitigate the adverse effects of such delays, a
novel predictor-observer structured controller is proposed which compensate for
both measurable output delays and unmeasurable, yet bounded, input delays
simultaneously. The study begins by novelly constructing an equivalen... more
This article is devoted to addressing the cloud control of connected
vehicles, specifically focusing on analyzing the effect of bi-directional
communication-induced delays. To mitigate the adverse effects of such delays, a
novel predictor-observer structured controller is proposed which compensate for
both measurable output delays and unmeasurable, yet bounded, input delays
simultaneously. The study begins by novelly constructing an equivalent
delay-free inter-connected system model that incorporates the
Predictor-Observer controller, considering certain delay boundaries and model
uncertainties. Subsequently, a stability analysis is conducted to assess the
system's robustness under these conditions. Next, the connected vehicle lateral
control scenario is built which contain high-fidelity vehicle dynamic model.
The results demonstrate the controller's ability to accurately predict the
system states, even under time-varying bi-directional delays. Finally, the
proposed method is deployed in a real connected vehicle lateral control system.
Comparative tests with a conventional linear feedback controller showcase
significantly improved control performance under dominant bi-directional delay
conditions, affirming the superiority of the proposed method against the delay.
less
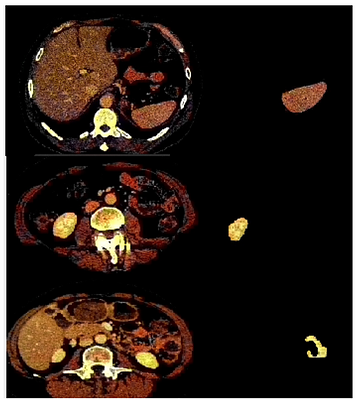
By: Alireza Ranjbaran, Azadeh Nazemi
An in-vitro cell culture system is used for biological discoveries and
hypothesis-driven research on a particular cell type to understand mechanistic
or test pharmaceutical drugs. Conventional in-vitro cultures have been applied
to primary cells and immortalised cell lines plated on 2D surfaces. However,
they are unreliable in complex physiological environments and can not always
predict in-vivo behaviour correctly. Organoids are multicellu... more
An in-vitro cell culture system is used for biological discoveries and
hypothesis-driven research on a particular cell type to understand mechanistic
or test pharmaceutical drugs. Conventional in-vitro cultures have been applied
to primary cells and immortalised cell lines plated on 2D surfaces. However,
they are unreliable in complex physiological environments and can not always
predict in-vivo behaviour correctly. Organoids are multicellular spheroids of a
primary donor or stem cells that are replaced in vitro cell culture systems and
are widely used in biological, biomedical and translational studies. Native
heterogeneity, microanatomy, and functionality of an organ or diseased tissue
can be represented by three-dimensional in-vitro tissue models such as
organoids. Organoids are essential in in-vitro models for drug discovery and
personalised drug screening. Many imaging artefacts such as organoid occlusion,
overlap, out-of-focus spheroids and considerable heterogeneity in size cause
difficulty in conventional image processing. Despite the power of organoid
models for biology, their size and shape have mostly not been considered. Drug
responses depend on dynamic changes in individual organoid morphology, number
and size, which means differences in organoid shape and size, movement through
focal planes, and live-cell staining with limited options cause challenges for
drug response and growth analysis. This study primarily introduces the
importance of the role of the organoid culture system in different disciplines
of medical science and various scopes of utilising organoids. Then studies the
challenges of operating organoids, followed by reviewing image analysis systems
or platforms applied to organoids to address organoid utilising challenges.
less
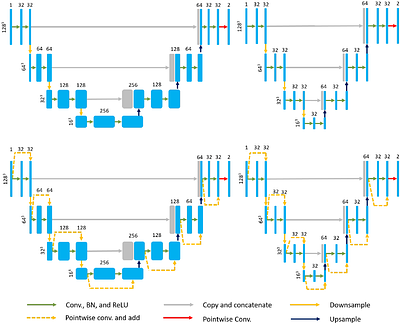
By: Adrian Celaya, Jonas A. Actor, Rajarajeswari Muthusivarajan, Evan Gates, Caroline Chung, Dawid Schellingerhout, Beatrice Riviere, David Fuentes
Medical imaging deep learning models are often large and complex, requiring
specialized hardware to train and evaluate these models. To address such
issues, we propose the PocketNet paradigm to reduce the size of deep learning
models by throttling the growth of the number of channels in convolutional
neural networks. We demonstrate that, for a range of segmentation and
classification tasks, PocketNet architectures produce results comparable... more
Medical imaging deep learning models are often large and complex, requiring
specialized hardware to train and evaluate these models. To address such
issues, we propose the PocketNet paradigm to reduce the size of deep learning
models by throttling the growth of the number of channels in convolutional
neural networks. We demonstrate that, for a range of segmentation and
classification tasks, PocketNet architectures produce results comparable to
that of conventional neural networks while reducing the number of parameters by
multiple orders of magnitude, using up to 90% less GPU memory, and speeding up
training times by up to 40%, thereby allowing such models to be trained and
deployed in resource-constrained settings.
less
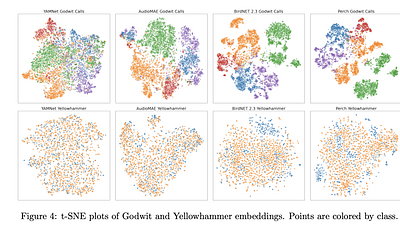
Feature Embeddings from Large-Scale Acoustic Bird Classifiers Enable Few-Shot Transfer Learning
1upvote
By: Burooj Ghani, Tom Denton, Stefan Kahl, Holger Klinck
Automated bioacoustic analysis aids understanding and protection of both
marine and terrestrial animals and their habitats across extensive
spatiotemporal scales, and typically involves analyzing vast collections of
acoustic data. With the advent of deep learning models, classification of
important signals from these datasets has markedly improved. These models power
critical data analyses for research and decision-making in biodiversity
mo... more
Automated bioacoustic analysis aids understanding and protection of both
marine and terrestrial animals and their habitats across extensive
spatiotemporal scales, and typically involves analyzing vast collections of
acoustic data. With the advent of deep learning models, classification of
important signals from these datasets has markedly improved. These models power
critical data analyses for research and decision-making in biodiversity
monitoring, animal behaviour studies, and natural resource management. However,
deep learning models are often data-hungry and require a significant amount of
labeled training data to perform well. While sufficient training data is
available for certain taxonomic groups (e.g., common bird species), many
classes (such as rare and endangered species, many non-bird taxa, and
call-type), lack enough data to train a robust model from scratch. This study
investigates the utility of feature embeddings extracted from large-scale audio
classification models to identify bioacoustic classes other than the ones these
models were originally trained on. We evaluate models on diverse datasets,
including different bird calls and dialect types, bat calls, marine mammals
calls, and amphibians calls. The embeddings extracted from the models trained
on bird vocalization data consistently allowed higher quality classification
than the embeddings trained on general audio datasets. The results of this
study indicate that high-quality feature embeddings from large-scale acoustic
bird classifiers can be harnessed for few-shot transfer learning, enabling the
learning of new classes from a limited quantity of training data. Our findings
reveal the potential for efficient analyses of novel bioacoustic tasks, even in
scenarios where available training data is limited to a few samples.
less
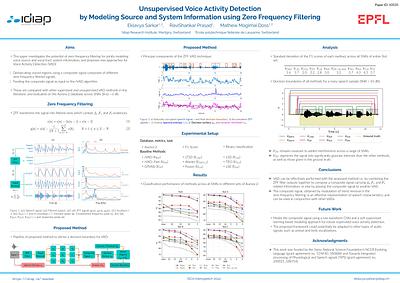
By: Eklavya Sarkar, RaviShankar Prasad, Mathew Magimai. -Doss
Voice activity detection (VAD) is an important pre-processing step for speech technology applications. The task consists of deriving segment boundaries of audio signals which contain voicing information. In recent years, it has been shown that voice source and vocal tract system information can be extracted using zero-frequency filtering (ZFF) without making any explicit model assumptions about the speech signal. This paper investigates the p... more
Voice activity detection (VAD) is an important pre-processing step for speech technology applications. The task consists of deriving segment boundaries of audio signals which contain voicing information. In recent years, it has been shown that voice source and vocal tract system information can be extracted using zero-frequency filtering (ZFF) without making any explicit model assumptions about the speech signal. This paper investigates the potential of zero-frequency filtering for jointly modeling voice source and vocal tract system information, and proposes two approaches for VAD. The first approach demarcates voiced regions using a composite signal composed of different zero-frequency filtered signals. The second approach feeds the composite signal as input to the rVAD algorithm. These approaches are compared with other supervised and unsupervised VAD methods in the literature, and are evaluated on the Aurora-2 database, across a range of SNRs (20 to -5 dB). Our studies show that the proposed ZFF-based methods perform comparable to state-of-art VAD methods and are more invariant to added degradation and different channel characteristics. less
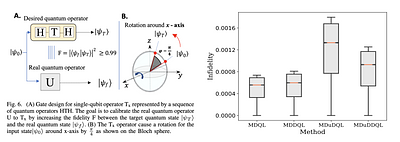
By: Omar Shindi, Qi Yu, Parth Girdhar, Daoyi Dong
High-fidelity quantum gate design is important for various quantum
technologies, such as quantum computation and quantum communication. Numerous
control policies for quantum gate design have been proposed given a dynamical
model of the quantum system of interest. However, a quantum system is often
highly sensitive to noise, and obtaining its accurate modeling can be difficult
for many practical applications. Thus, the control policy based o... more
High-fidelity quantum gate design is important for various quantum
technologies, such as quantum computation and quantum communication. Numerous
control policies for quantum gate design have been proposed given a dynamical
model of the quantum system of interest. However, a quantum system is often
highly sensitive to noise, and obtaining its accurate modeling can be difficult
for many practical applications. Thus, the control policy based on a quantum
system model may be unpractical for quantum gate design. Also, quantum
measurements collapse quantum states, which makes it challenging to obtain
information through measurements during the control process. In this paper, we
propose a novel training framework using deep reinforcement learning for
model-free quantum control. The proposed framework relies only on the
measurement at the end of the control process and offers the ability to find
the optimal control policy without access to quantum systems during the
learning process. The effectiveness of the proposed technique is numerically
demonstrated for model-free quantum gate design and quantum gate calibration
using off-policy reinforcement learning algorithms.
less
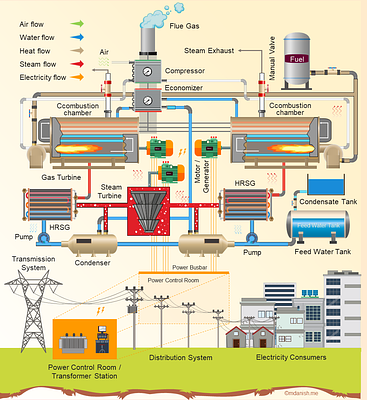
By: Mir Sayed Shah Danish, Zahra Nazari, Tomonobu Senjyu
This study investigates the transformation of energy models to align with
machine learning requirements as a promising tool for optimizing the operation
of combined cycle power plants (CCPPs). By modeling energy production as a
function of environmental and control variables, this methodology offers an
innovative way to achieve energy-efficient power generation in the context of
the data-driven application. This study focuses on developing ... more
This study investigates the transformation of energy models to align with
machine learning requirements as a promising tool for optimizing the operation
of combined cycle power plants (CCPPs). By modeling energy production as a
function of environmental and control variables, this methodology offers an
innovative way to achieve energy-efficient power generation in the context of
the data-driven application. This study focuses on developing a thorough
AI-coherent modeling approach for CCPP optimization, preferring an
interdisciplinary perspective and coming up with a comprehensive, insightful
analysis. The proposed numerical model using Broyden Fletcher Goldfarb Shanno
(BFGS) algorithm enhances efficiency by simulating various operating scenarios
and adjusting optimal parameters, leading to a high yield power generation of
2.23% increase from 452 MW to 462.1 MW by optimizing the environmental factors.
This study deals with data-driven modeling based on historical data to make
predictions without prior knowledge of the system's parameter, demonstrating
several merits in identifying patterns that can be difficult for human analysts
to detect, high accuracy when trained on large datasets, and the potential to
improve over time with new data. The proposed modeling approach and methodology
can be expanded as a valuable tool for forecasting and decision-making in
complex energy systems.
less
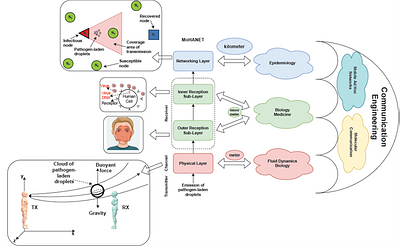
By: Fatih Gulec, Baris Atakan, Falko Dressler
A number of transmission models for airborne pathogens transmission, as
required to understand airborne infectious diseases such as COVID-19, have been
proposed independently from each other, at different scales, and by researchers
from various disciplines. We propose a communication engineering approach that
blends different disciplines such as epidemiology, biology, medicine, and fluid
dynamics. The aim is to present a unified framework u... more
A number of transmission models for airborne pathogens transmission, as
required to understand airborne infectious diseases such as COVID-19, have been
proposed independently from each other, at different scales, and by researchers
from various disciplines. We propose a communication engineering approach that
blends different disciplines such as epidemiology, biology, medicine, and fluid
dynamics. The aim is to present a unified framework using communication
engineering, and to highlight future research directions for modeling the
spread of infectious diseases through airborne transmission. We introduce the
concept of mobile human ad hoc networks (MoHANETs), which exploits the
similarity of airborne transmission-driven human groups with mobile ad hoc
networks and uses molecular communication as the enabling paradigm. In the
MoHANET architecture, a layered structure is employed where the infectious
human emitting pathogen-laden droplets and the exposed human to these droplets
are considered as the transmitter and receiver, respectively. Our
proof-of-concept results, which we validated using empirical COVID-19 data,
clearly demonstrate the ability of our MoHANET architecture to predict the
dynamics of infectious diseases by considering the propagation of
pathogen-laden droplets, their reception and mobility of humans.
less