Cardiomyocyte-specific expression of HIF-1α mediates the cardioprotective effects of Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH)
Cardiomyocyte-specific expression of HIF-1α mediates the cardioprotective effects of Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH)
Takeuchi, R. M. K.; Takeuchi, L. M.; Balkan, W.; Wanschel, A.; Hatzistergos, K. E.; Kulandavelu, S.; Saltzman, R. G.; Shehadeh, L. A.; Sha, W.; Schally, A. V.; Kurtenbach, S.; Hare, J. M.
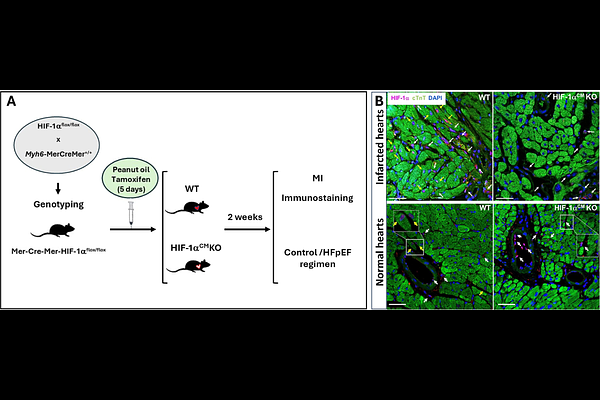
AbstractHeart failure (HF) with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) carries a high mortality and remains a major therapeutic challenge. Effective, targeted therapies capable of reversing HFpEF pathophysiology are urgently needed. We previously demonstrated that activation of the cardiac growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) pathway using high potency synthetic agonists of GHRH (GHRH-agonists: MR-356 and MR-409) improves the HFpEF phenotype in both large and small animal models, including in a murine model of cardiometabolic HFpEF (High fat diet + the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-NAME [HFD+L-NAME]). Here we sought to define the downstream signaling pathways responsible for this effect. A transcriptomic screen in human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) identified the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 pathway as being activated by GHRH receptor (GHRHR) signaling, revealing an oxygen-independent mechanism of HIF-1 activation. Based on this finding, we investigated the interaction between the cardioprotective effects of the GHRH-agonist MR-356 and HIF-1 pathway activation in the murine HFD+L-NAME model of cardiometabolic HFpEF. We generated a cardiomyocyte-specific HIF-1 knockout (HIF-1CMKO) mouse line and demonstrated that our previously reported beneficial effects of GHRH-agonist administration were completely abolished in HIF-1CMKO mice. Together, these findings establish the GHRHR-HIF-1 axis as a central pathway integrating metabolic and contractile remodeling, suggesting that therapeutic targeting of this axis represents a novel disease-modifying approach to treating cardiometabolic HFpEF.