Whole-genome prediction of bacterial pathogenic capacity on novel bacteria using protein language models, with PathogenFinder2
Whole-genome prediction of bacterial pathogenic capacity on novel bacteria using protein language models, with PathogenFinder2
Ferrer Florensa, A.; Almagro Armenteros, J. J.; Kaas, R. S.; Clausen, P. T.; Nielsen, H.; Rost, B.; Aarestrup, F. M.
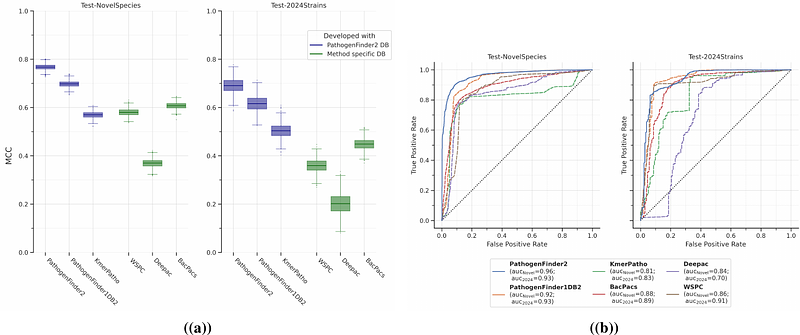
AbstractInfectious diseases continue to be a leading cause of mortality and pose a significant global health threat. Thus the development of tools for surveillance and early detection of emerging pathogens is needed. In this study, we introduce PathogenFinder2, a novel predictor of bacterial pathogenic capacity in humans, available through an online server (http://genepi.food.dtu.dk/pathogenfinder2), or as a standalone program (https://github.com/genomicepidemiology/PathogenFinder2). The model, using protein language models for whole-genome phenotype prediction, surpasses the performance of previous methods, especially for novel bacterial taxa, while being taxonomy-agnostic and alignment-free. At the same time, it predicts the importance of each protein for the pathogenic capacity. This output might aid in characterizing potential pathogens, it readily identifies new candidates for virulence factors and vaccine targets and offers insights into infection metabolic pathways. Furthermore, we introduce the Bacterial Pathogenic Landscape, revealing distributions related to the host conditions, antagonist bacteria, infection site, or habitat.