G-quadruplex structures regulate long-range transcriptional reprogramming to promote drug resistance in ovarian cancer
G-quadruplex structures regulate long-range transcriptional reprogramming to promote drug resistance in ovarian cancer
Robinson, J.; Flint, G.; Garner, I.; Galli, S.; Maher, T.; Kuimova, M.; Vilar, R.; McNeish, I.; Brown, R.; Keun, H. C.; Di Antonio, M.
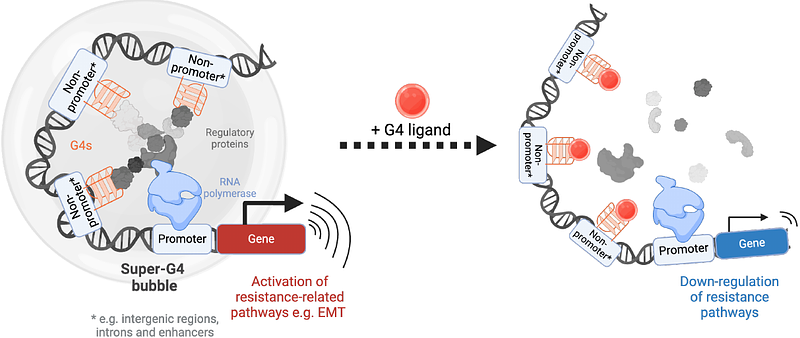
AbstractEpigenetic evolution is a common mechanism used by cancer cells to evade the therapeutic effects of drug treatment. In ovarian cancers, epigenetically-driven resistance may be responsible for a large number of late-stage patient deaths. Here, we describe the first investigation into the role of G-quadruplex (G4) DNA secondary structures in mediating epigenetic regulation in drug-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Through genome-wide mapping of G4s in paired drug-sensitive and drug-resistant cell lines, we find that increased G4 formation is associated with significant increase in gene expression, with high enrichment in signalling pathways previously established to promote drug-resistant states. However, in contrast to previous studies, the expression-enhancing effects of G4s were not found at gene promoters, but intergenic and intronic regions, indicating that G4s promote long-range transcriptional regulation in drug-resistant cells. Furthermore, we discovered that clusters of G4s (super-G4s) are associated with particularly high levels of transcriptional enhancement that surpass the effects of super-enhancers, which act as well established regulatory sites in many cancers. Finally, we demonstrate that targeting G4s with small molecules results in significant down-regulation of pathways associated with drug-resistance, which results in resensitisation of resistant cells to chemotherapy agents. These findings indicate that G4 structures are critical for the epigenetic regulatory networks of drug-resistant cells and may represent a promising target to treat drug-tolerant ovarian cancer.


