rDNAcaller: a fast and robust pipeline to call ribosomal DNA variants
rDNAcaller: a fast and robust pipeline to call ribosomal DNA variants
Ramirez, J. M.; Oliveros, W.; Garcia-Perez, R.; Jimenez-Lupianez, A.; Shah, A.; Perez-Cano, P.; Reese, F.; Vazquez, M.; Mele, M.
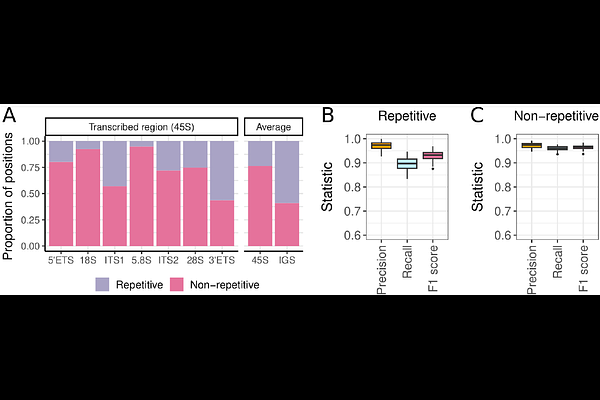
AbstractRibosomal DNA (rDNA) genes are essential components of the ribosome, organized as tandem repeats on the mammalian genomes. Extensive genetic and copy number variation in rDNA has been reported both within and between individuals, contributing to phenotypic diversity. However, previous rDNA variant calling strategies have relied on methods designed for diploid regions and have not been systematically benchmarked. With the recent availability of a telomere-to-telomere (T2T) genome assembly, rDNA regions have been fully assembled for the first time, enabling benchmarking and optimization of rDNA variant calling strategies. We developed a customized simulator that replicates real intra- and inter-individual rDNA variation based on the T2T assembly to benchmark the performance of commonly used variant callers, including GATK, Mutect2, and Lofreq. Additionally, we optimized the preprocessing and mapping steps to remove pseudogenes and significantly improve accuracy. Based on these optimizations, we introduce rDNAcaller, a novel pipeline for accurate rDNA variant detection using short-read whole-genome sequencing. rDNAcaller integrates optimized preprocessing with the top-performing variant caller and achieves 94% precision on experimental data from the T2T cell line. Applying our pipeline to data from the 1000 Genomes Project, we identify 5,607 novel rDNA variant positions across human populations, with African individuals showing the highest number of variants. Overall, rDNAcaller is a robust and versatile tool for analyzing rDNA variation, addressing the limitations of existing methods in handling high ploidies. By enabling accurate detection of rDNA variants, it facilitates deeper exploration of rDNA\'s role in phenotypic diversity, supporting future genomic studies and broadening our understanding of rDNA biology in health and disease.