Rescue of lysosomal acid lipase deficiency in mice by rAAV8 liver gene transfer.
Rescue of lysosomal acid lipase deficiency in mice by rAAV8 liver gene transfer.
Laurent, M.; Harb, R.; Jenny, C.; Oustelandt, J.; Jimenez, S.; Cosette, J.; Landini, F.; Ferrante, A.; Corre, G.; Vujic, N.; Piccoli, C.; Brassier, A.; Van Wittenberghe, L.; Ronzitti, G.; Kratky, D.; Pacelli, C.; Amendola, M.
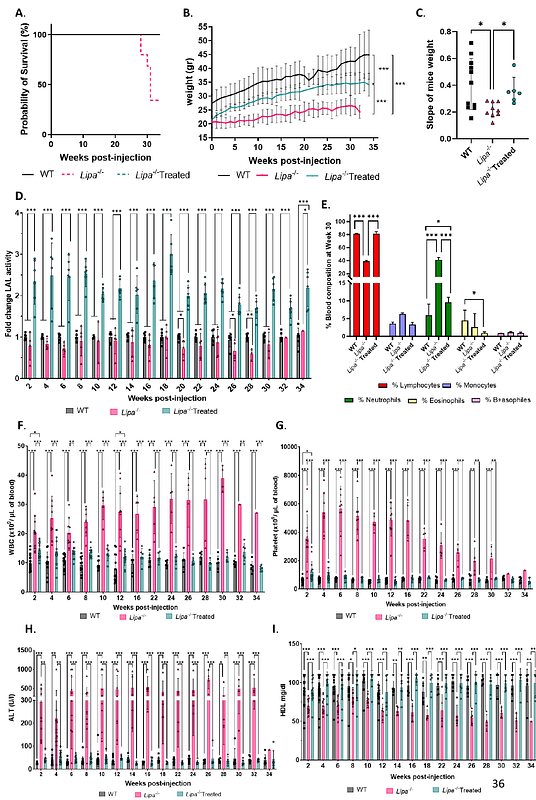
AbstractLysosomal acid lipase deficiency (LAL-D) is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the LIPA gene, which results in lipid accumulation leading to multi-organ failure. If left untreated, the severe form of LAL-D results in premature death within the first year of life due to failure to thrive and hepatic insufficiency. Enzyme replacement therapy is the only available supportive treatment consisting in weekly systemic injections of recombinant LAL protein. Here, we characterized a novel Lipa-/- mouse model and developed a curative gene therapy treatment based on the in vivo administration of recombinant (r)AAV8 vector encoding the human LIPA transgene under the control of a hepatocyte-specific promoter. We defined the minimal rAAV8 dose required to rescue disease lethality and to correct cholesterol and triglyceride accumulation in multiple organs and blood. Finally, using liver transcriptomic and biochemical analysis, we showed mitochondrial impairment in Lipa-/- mice and its recovery by gene therapy. Overall, our in vivo gene therapy strategy achieves a stable long-term LAL expression sufficient to correct the disease phenotype in the Lipa-/- mouse model and offers a new therapeutic option for LAL-D patients.
