HIF1α and HIF2α mRNA Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma does not correlate with protein expression
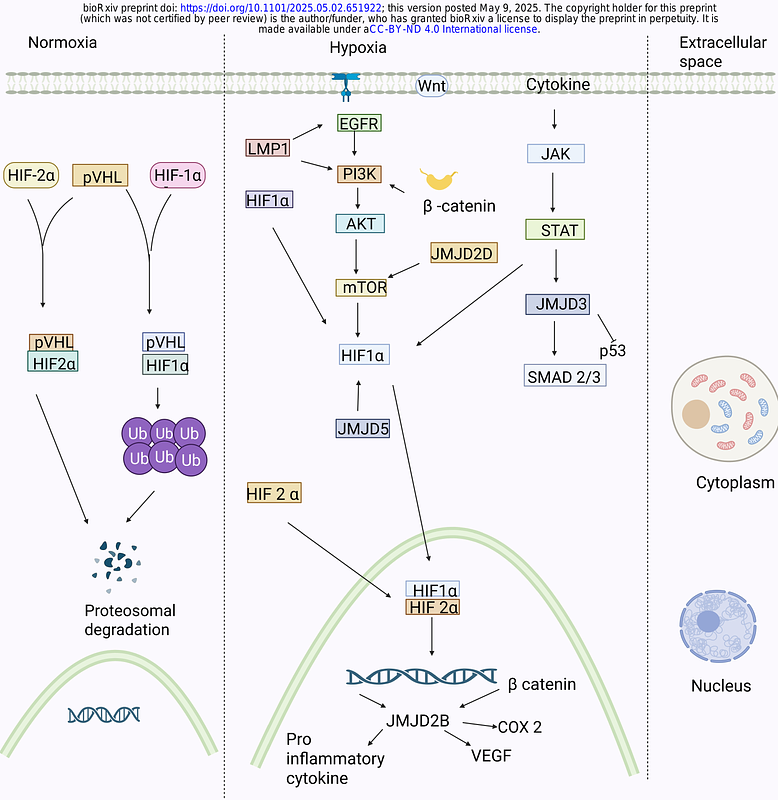
HIF1α and HIF2α mRNA Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma does not correlate with protein expression
Pandey, M.; Singh, P.; Nath, G.; Kumar, D.; Kar, A. G.
AbstractBackground: Oral cancer is one of the common cancers among men, its presentation is usually late. Tumor growth leads to hypoxia, and HIF1 and HIF2 are important regulators of hypoxia induced pathways, inducing angiogenesis and tumor growth. This study compares the expression levels of HIF1 and HIF2 mRNA in OSCC tissues to adjacent normal mucosa. Methods: RNA was isolated from 85 OSCC tissues and adjacent normal mucosa followed by real-time (RT) PCR to quantify HIF1 and HIF2 expression using GAPDH and -actin respectively as reference genes. Results: HIF1 overexpression was detected in 76.47% of case and 71.76% of controls (p=0.4906), whereas HIF2 overexpression occurred in 91.76% of cases 94.11% of controls (p=0.35). HIF1 and HIF2 expression level were not significantly different in OSCC tissues compared to adjacent normal mucosa. Conclusion: HIF1 and HIF2 play important role in hypoxia induced pathways and tumor progression, yet this study found no significant variation in expression between OSCC tissues and surrounding normal tissues. This suggest that their expression may be due to physiological adaptability to hypoxia or stress, or may be due to use of adjacent tissue as control and loss of protein expression could be due to post translational modifications.