In Silico Tool for Predicting and Scanning Rheumatoid Arthritis-Inducing Peptides in an Antigen
In Silico Tool for Predicting and Scanning Rheumatoid Arthritis-Inducing Peptides in an Antigen
Tomer, R.; Jain, S.; Gahlot, P. S.; Bajiya, N.; Raghava, G. P. S.
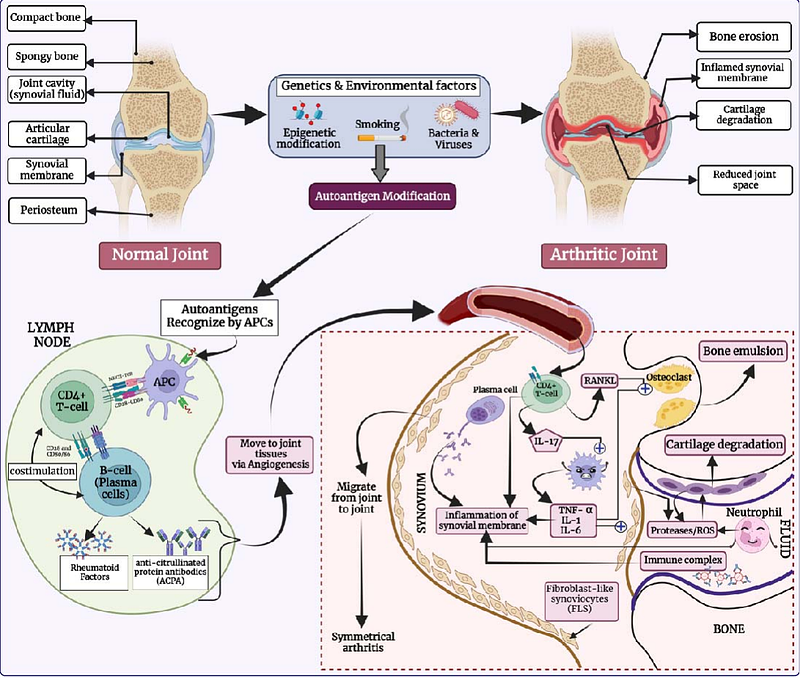
AbstractRheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mounts an abnormal response to self-antigens, leading to chronic inflammation and joint damage. Therefore, identifying antigenic regions in a protein that trigger RA is crucial for developing protein-based therapeutics. In this study, we developed models for predicting RA-inducing peptides using a dataset comprising of 291 experimentally confirmed RA-inducing peptides and 165 RA non-inducing peptides. Our initial analysis revealed that certain residues, such as glycine, proline, and tyrosine, are significantly enriched in RA-inducing peptides. While alignment-based techniques like BLAST and MERCI offered high precision, they suffered from limited coverage. We developed machine/deep learning based prediction and obtained highest performance (AUC = 0.75) using XGboost on an independent dataset. We also developed prediction methods using large language models and achieved highest performance (AUC 0.72) using ProtBERT. Our ensemble model achieved highest performance (AUC = 0.80 & MCC = 0.45) on an independent dataset that combine XGBoost and MERCI-derived motifs. All models were rigorously evaluated on an independent dataset not used during training or testing of models. This study will be valuable for assessing the risk of proteins used in probiotics, genetically modified foods, and protein-based therapeutics. Our most effective approach has been implemented in RAIpred, a web server and standalone software tool for predicting and scanning RA-inducing peptides. (https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/raipred/).