Rosace-AA: Enhancing Interpretation of Deep Mutational Scanning Data with Amino Acid Substitution and Position-Specific Insights
Rosace-AA: Enhancing Interpretation of Deep Mutational Scanning Data with Amino Acid Substitution and Position-Specific Insights
Rao, J.; Wang, M.; Howard, M. K.; Macdonald, C.; Fraser, J.; Coyote-Maestas, W.; Pimentel, H.
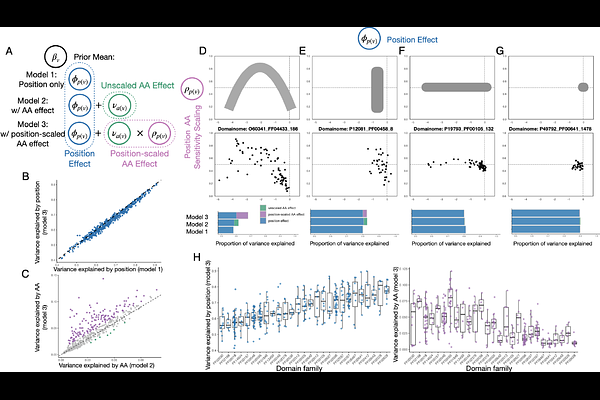
AbstractProteins are dynamic systems whose function and behavior are sensitive to environmental conditions and often involve multiple cellular roles. Deep mutational scanning (DMS) experiments generate extensive datasets to capture the functional consequences of mutations. However, the sheer volume of data presents challenges in visualization and interpretation. Current approaches often rely on heatmaps, but these methods fail to capture the nuanced effects of amino acid (AA) substitutions, which are essential for understanding mutational impact. To address this, we extend the Rosace framework with RosaceAA, a model that incorporates both position-specific information and AA substitution trends. Using substitution matrices like BLOSUM90, RosaceAA offers a flexible and interpretable approach to summarize DMS data on both protein-level and position-level. We demonstrate its utility across datasets, including OCT1 and MET kinase, showing that RosaceAA highlights key positions where mutations deviate from expected substitution patterns and captures functionally relevant variation in protein behavior across multiple DMS screens. These results suggest that RosaceAA enables more robust and interpretable analysis of complex DMS datasets.