AURKA inhibition amplifies DNA replication stress to foster WEE1 kinase dependency and synergistic antitumor effects with WEE1 inhibition in cancers
AURKA inhibition amplifies DNA replication stress to foster WEE1 kinase dependency and synergistic antitumor effects with WEE1 inhibition in cancers
Lee, J. W.; Shi, J.; Barrantes, J.; Chaurasia, P.; Kim, S.; Cruz-Gomez, S.; Yang, C.; Gu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, D.; Schiff, B.; Roche, A.; Perry, E. B.; Townsend, J. P.; Kupfer, G. M.; Politi, K.; Golemis, E.; Burtness, B.
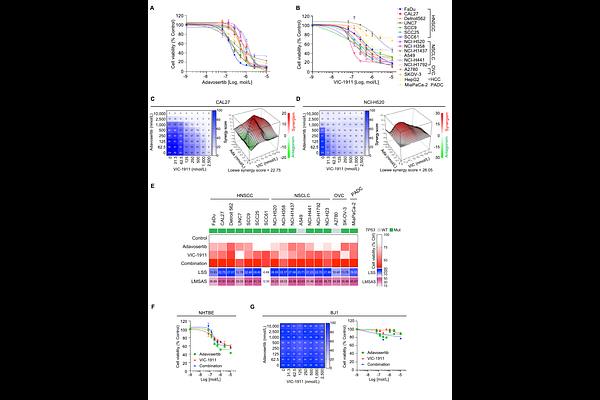
AbstractHighly elevated expression of the oncogene Aurora kinase A (AURKA) occurs in numerous human cancers harboring defective p53, nominating AURKA as a potential vulnerability in TP53-mutated cancer. However, clinical trials have indicated modest monotherapy activity of AURKA inhibitors. Here, we demonstrate that AURKA inhibition promotes phosphorylation of Replication Protein A (RPA), resulting in stalled DNA replication fork progression and eliciting a replication stress response in multiple TP53-mutated models, creating a druggable dependence on the mitotic checkpoint kinase WEE1. Combined inhibition of AURKA and WEE1 synergistically enhanced replication stress, tumor-specific apoptotic cell death, and mitotic catastrophe, and led to marked tumor regression in cell line- and patient-derived xenograft models of TP53-mutated cancer. Our findings define enhanced DNA replication stress as underlying the strong synergy between AURKA and WEE1 inhibitors and offer preclinical confirmation of efficacy, indicating high potential for clinical translation of this synthetic lethal strategy for TP53-mutated carcinomas.