Genetic Code Expansion and Enzymatic Modifications as Accessible Methods for Studying Site-Specific Post-Translational Modifications of Alpha-Synuclein and Tau
Genetic Code Expansion and Enzymatic Modifications as Accessible Methods for Studying Site-Specific Post-Translational Modifications of Alpha-Synuclein and Tau
Saleh, I. G.; Shimogawa, M.; Ramirez, J.; Abakah, B.; Venkatesh, Y.; James, H. P.; Li, M.-H.; Louie, S.; Lougee, M. G.; Chia, W.-K.; Cooley, R. B.; Mehl, R.; Baumgart, T.; Mach, R.; Eliezer, D.; Rhoades, E.; Petersson, E. J.
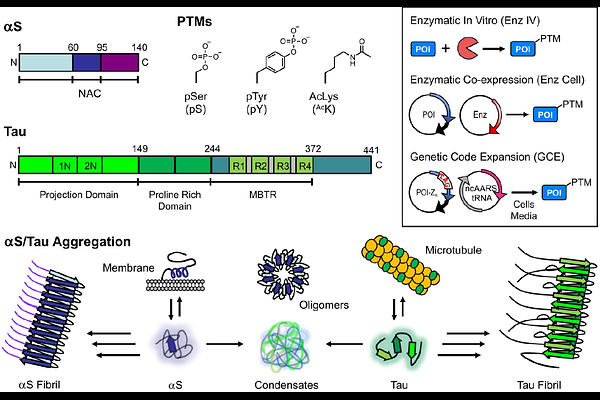
AbstractAlpha-synuclein (S) and tau play important roles in the pathology of Parkinson\'s Disease and Alzheimer\'s Disease, respectively, as well as numerous other neurodegenerative diseases. Both proteins are classified as intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs), as they have no stable structure that underlies their function in healthy tissue, and both proteins are prone to aggregation in disease states. There is substantial interest in understanding the roles that post-translational modifications (PTMs) play in regulating the structural dynamics and function of S and tau monomers, as well as their propensity to aggregate. While there have been many valuable insights into site-specific effects of PTMs garnered through chemical synthesis and semi-synthesis, these techniques are often outside of the expertise of biochemistry and biophysics laboratories wishing to study S and tau. Therefore, we have assembled a primer on genetic code expansion and enzymatic modification approaches to installing PTMs into S and tau site-specifically, including isotopic labeling for NMR and fluorescent labeling for biophysics and microscopy experiments. These methods should be enabling for those wishing to study authentic PTMs in S or tau as well as the broader field of IDPs and aggregating proteins.