CHARON: Estimating the drift time and the number of individuals in environmental DNA with diploid individuals
CHARON: Estimating the drift time and the number of individuals in environmental DNA with diploid individuals
van Waaij, J.; Hartmann, M. V.; Sackett, P. W.; Renaud, G.
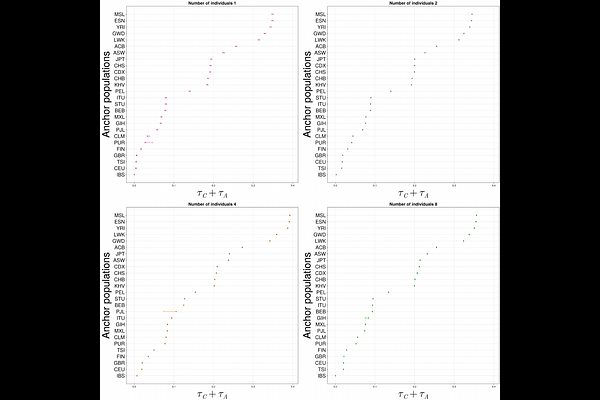
AbstractEnvironmental DNA (eDNA) offers a promising avenue for reconstructing the genetic diversity and demographic history of ancient populations. However, the analysis of eDNA from humans or forensic DNA, presents significant challenges, including low coverage, DNA degradation, and the uncertainty of the number of individuals contributing to a sample. This study introduces CHARON, a novel statistical method for jointly estimating the number of individuals and drift times between a human eDNA or forensic sample and a given population with known allele frequencies. We validate our method through simulations and synthetic empirical data and show that we can reliably estimate the number of individuals up to 8 at a coverage between 2X and 4X. Our method can also pinpoint the most likely population of origin for eDNA or forensic samples. This work provides a tool for the application of human eDNA in evolutionary and forensic studies and an implementation is available here: https://github.com/Jan-van-Waaij/Charon.