MPBind: Multitask Protein Binding Site Prediction by Protein Language Models and Equivariant Graph Neural Networks
MPBind: Multitask Protein Binding Site Prediction by Protein Language Models and Equivariant Graph Neural Networks
wang, y.; Boadu, F.; Cheng, J.
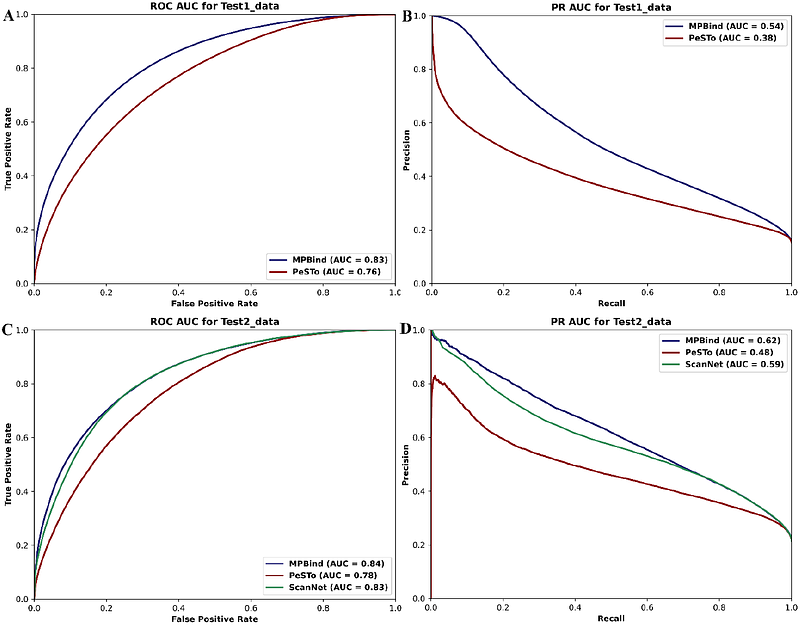
AbstractProteins interact with a variety of molecules, including other proteins, DNAs, RNAs, ligands, ions, and lipids. These interactions play a crucial role in cellular communication, metabolic regulation, immune response, and structural integrity, making proteins fundamental to nearly all biological functions. Accurately predicting protein binding (interaction) sites is essential for understanding protein interactions and functions. Here, we introduce MPBind, a multitask protein binding site prediction method, which integrates protein language models (PLMs) that can extract structural and functional information from sequences and equivariant graph neural networks (EGNNs) that can effectively capture geometric features of 3D protein structures. Through multitask learning, it can predict binding sites on proteins that interact with five key categories of binding partners: proteins, DNA/RNA, ligands, lipids, and ions, which is more comprehensive than most existing task-specific methods that can predict only one or a few kinds of binding sites. Moreover, MPBind outperforms both general bind site prediction methods and task-specific binding site prediction methods.