Destabilized host-parasite dynamics in newly founded populations
Destabilized host-parasite dynamics in newly founded populations
Bolnick, D. I.; Barrett, R.; Choi, E.; Eckert, L.; Hendry, A.; Kerns, E. V.; Lind, A.; Milligan-McClellan, K.; Peichel, C.; Sasser, K. T.; Wolf, C.; Steinel, N.; Weber, J. N.
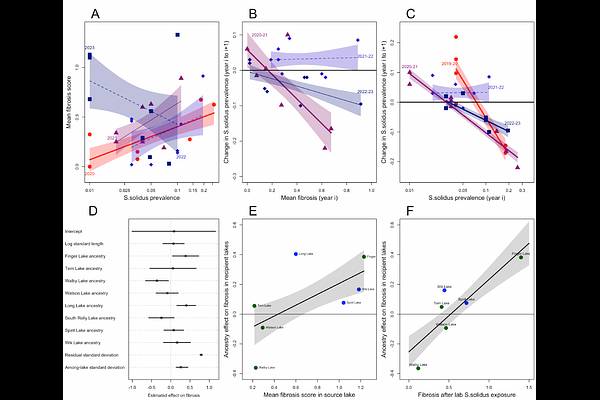
AbstractWhen species disperse into previously unoccupied habitats, new populations encounter unfamiliar species interactions such as altered parasite loads. Theory predicts that newly founded populations should exhibit destabilized eco-evolutionary fluctuations in infection rates and immune traits. However, to understand founder effects biologists typically rely on retrospective studies of range expansions, missing early-generation infection dynamics. To remedy this, we experimentally founded whole-lake populations of threespine stickleback. Infection rates were temporally stable in native source lakes. In contrast, newly founded populations exhibit destabilized host-parasite dynamics: high starting infection rates led to increases in a heritable immune trait (peritoneal fibrosis), suppressing infection rates. The resulting temporal auto-correlation between infection and immunity suggest that newly founded populations can exhibit rapid host-parasite eco-evolutionary dynamics.