T2R5 agonist phendione decreases cell viability and induces apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
T2R5 agonist phendione decreases cell viability and induces apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Sywanycz, S.; Hill, B. L.; Miller, Z. A.; Turner, G.; Huang, L.; Polen, K.; Lee, R. J.; Carey, R. M.
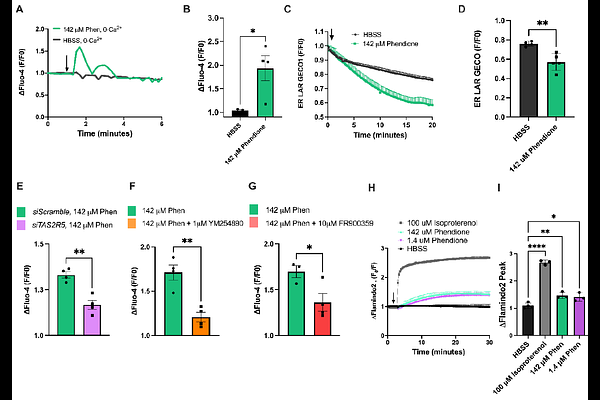
AbstractBitter taste receptors (T2Rs), a family of G-protein coupled receptors, are emerging as potential therapeutic targets in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Phendione, a known T2R5 agonist, has not been previously investigated in HNSCC. Here, we show that phendione activates endogenously expressed T2R5 in HNSCC cells and ex vivo tumor samples, inducing sustained calcium responses, reducing cell viability, and promoting apoptosis through a T2R5-dependent mechanism. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas data revealed that high T2R5 expression in HNSCC tumors correlates with improved long-term disease-specific survival, suggesting a potential tumor-suppressive role for T2R5. These findings highlight T2R5 as a promising therapeutic target in HNSCC and support further investigation of phendione or other T2R5 agonists as potential anti-cancer agents.