ADGRE5 ACTS AS A MELANOMA TUMOR SUPPRESSOR IN NATURALLY HYBRIDIZING XIPHOPHORUS.
ADGRE5 ACTS AS A MELANOMA TUMOR SUPPRESSOR IN NATURALLY HYBRIDIZING XIPHOPHORUS.
Garcia-Olazabal, M.; Adolfi, M. C.; Wilde, B.; Hufnagel, A.; Paudel, R.; Lu, Y.; Meierjohann, S.; Rosenthal, G. G.; Schartl, M.
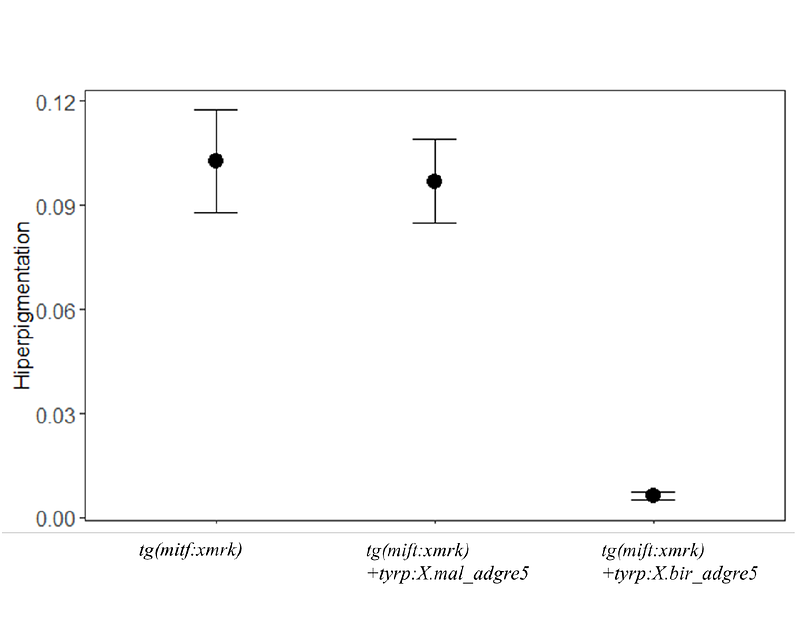
AbstractThe Xiphophorus genus has long been studied for its development of melanoma. xmrk has been identified as a potent oncogene. The recent discovery of adgre5 as a candidate tumor regulator gene in naturally hybridizing Xiphophorus birchmanni and X. malinche has shed new light on the genetic basis of melanoma. This study aimed to functionally test the role of the adgre5 alleles from each hybridizing species by analyzing their effect independently on cell growth and migration in vitro and melanoma development in vivo. In vitro experiments showed that cells with the X. birchmanni allele grew and migrated slower than those with the X. malinche allele. In vivo experiments using transgenic medaka confirmed that melanoma development was only inhibited in the presence of the X. birchmanni allele of adgre5. These findings provide new insights into the genetic basis of melanoma development in Xiphophorus and highlight the importance of adgre5 as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of melanoma.