Repurposing statins in combination therapy for effective ablation of metastatic breast cancer
Repurposing statins in combination therapy for effective ablation of metastatic breast cancer
Aara, R.; Sinai Borker, N.; Sajimon, J.; Subhadarshini, S.; VP, S.; Nimbalkar, V.; Moorthy, M.; P Thankamony, A.; Krishnan R, A.; Aich, D.; Das, D.; Jolly, M. K.; Prabhu, J. S.; Nair, R.
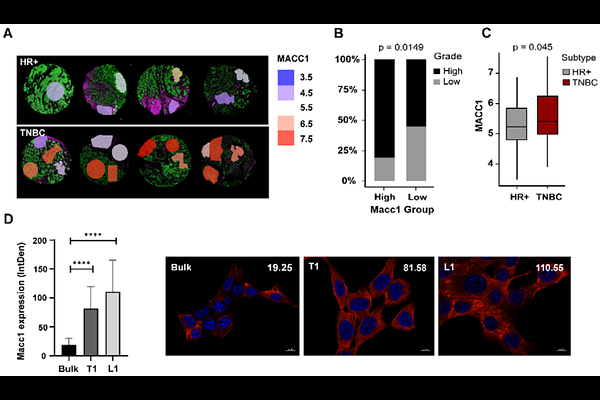
AbstractMetastatic breast cancer (mBC) remains an incurable disease with limited treatment options, highlighting the need for novel therapeutic approaches. Combination therapy with chemotherapeutic agents along with targeted therapy are the most common methods of treatment used in the terminal stages of the disease. Eventual development of resistance to these approaches, leading to fatal outcomes suggests the presence or emergence of a heterogenous population of cells intrinsically resistant to commonly used regimens. Previous work identified a heterogeneous population of metastatic tumor cells with distinct molecular characteristics driven by Macc1 (Metastasis Associated in Colon Cancer 1) overexpression, which could be targeted by lovastatin (transcriptional inhibitor of Macc1). Building on this foundation, the efficacy of lovastatin in targeting metastatic cells with high Macc1 expression was evaluated in lung metastasis, and the regulatory pathways governing Macc1 expression and lovastatin treatment in mBC were investigated. The expression of Macc1, in breast cancer biopsies provides insights into the intra and inter tumor heterogeneity of the Macc1 gene and its correlation with disease outcomes. While some studies suggest synergistic effects between statins and chemotherapeutic agents, comprehensive evaluations of various combinations and their therapeutic outcomes are still needed. The therapeutic efficacy of lovastatin combined with chemotherapy to determine the most effective treatment regimen that maximizes tumor cell ablation demonstrated that lovastatin can effectively ablate the chemoresistant tumor cells in mBC. The translational implications of this research will identify patient subgroups that may benefit most from statin-chemotherapy combinations that could support the repurposing of statins as cost-effective adjuvant therapies for mBC.