Analysis of Post-Translational Modifications in the Urinary Proteome of Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats (SHRSP)
Analysis of Post-Translational Modifications in the Urinary Proteome of Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats (SHRSP)
Su, Y.; Gao, Y.
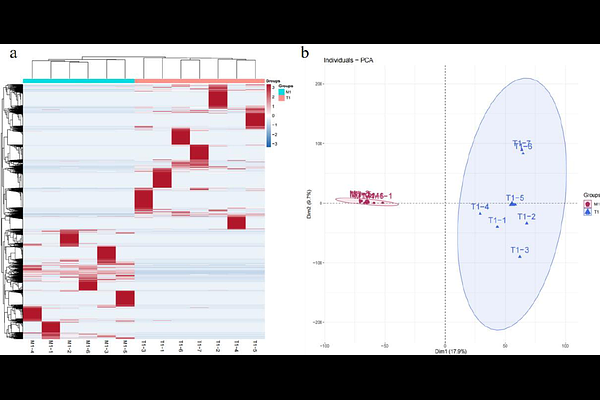
AbstractHypertension, one of the most prevalent chronic non-communicable diseases worldwide, is a primary risk factor for stroke and coronary heart disease. This study investigated dynamic changes in protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) and associated biological processes during hypertension progression by comparing urinary proteome PTMs between stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRSP) and normal rats at 1-, 8-, and 14-15-month-old stages. Results revealed both stage-specific and shared PTM alterations across hypertensive phases. Notably, multiple differentially modified proteins identified here have been previously implicated in hypertension pathogenesis or progression. Randomized group validation demonstrated that more than 95% of differential modifications between the hypertensive and control groups exhibited non-random characteristics. Furthermore, proteins harboring differential PTMs were significantly enriched in hypertension-related biological pathways and KEGG pathways, including regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure, renin-angiotensin system (RAS), and complement and coagulation cascades. These results highlight distinct urinary proteome PTM profiles between SHRSP and normal rats, providing new insights into the mechanisms of hypertension.