Medulloblastoma Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Tumor Microenvironment Heterogeneity with High-Density Progenitor Cell Regions Correlating with High-Risk Disease
Medulloblastoma Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Tumor Microenvironment Heterogeneity with High-Density Progenitor Cell Regions Correlating with High-Risk Disease
Chien, F.; Michaud, M. E.; Bakhtiari, M.; Schroff, C.; Snuderl, M.; Velazquez Vega, J. E.; MacDonald, T. J.; Bhasin, M. K.
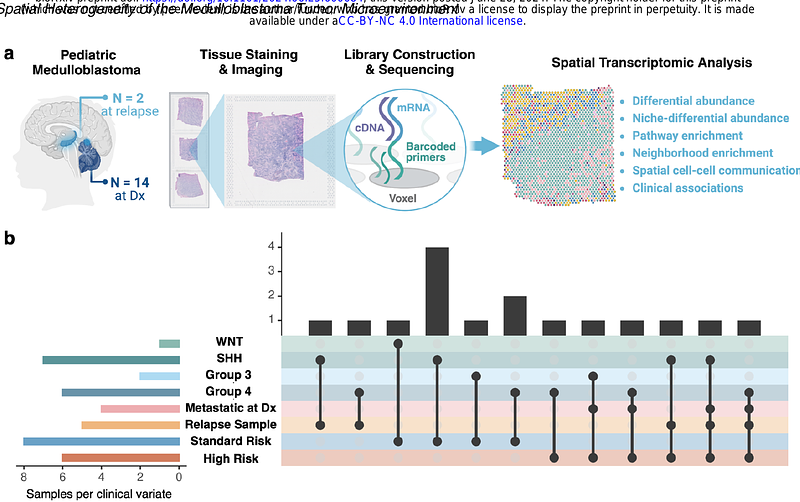
AbstractThe tumor microenvironment (TME) of medulloblastoma (MB) significantly influences tumor progression and therapy response, presenting a promising target for therapeutic advances. Prior single-cell analyses have characterized the cellular components of the TME but lack spatial context. To address this, we performed spatial transcriptomic sequencing on sixteen pediatric MB samples obtained at diagnosis, including two matched diagnosis-relapse pairs. Our analyses revealed inter- and intra-tumoral heterogeneity within the TME, comprised of tumor-associated astrocytes (TAAs), macrophages (TAMs), stromal components, and distinct subpopulations of MB cells at different stages of neuronal differentiation and cell cycle progression. Notably, we identified dense regions of quiescent progenitor-like MB cells enriched in patients with high-risk (HR) features and an increase in TAAs, TAMs, and dysregulated vascular endothelium following relapse. Our study presents novel insights into the spatial architecture and cellular landscape of the medulloblastoma TME, highlighting spatial patterns linked to HR features and relapse, which may serve as potential therapeutic targets.


