Structure of the γ-tubulin ring complex-capped microtubule
Structure of the γ-tubulin ring complex-capped microtubule
Aher, A.; Urnavicius, L.; Xue, A.; Neselu, K.; Kapoor, T.
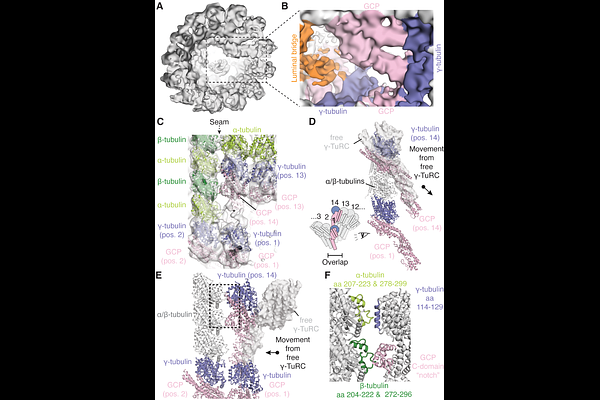
AbstractMicrotubules are composed of /{beta}-tubulin dimers positioned head-to-tail to form protofilaments that associate laterally in varying numbers. It is not known how cellular microtubules assemble with the canonical 13-protofilament architecture, resulting in micrometer-scale /{beta}-tubulin tracks for intracellular transport that align with, rather than spiral along, the filament\'s long-axis. We report that the human ~2.3MDa {gamma}-tubulin ring complex ({gamma}-TuRC), an essential regulator of microtubule formation that contains 14 {gamma}-tubulins, selectively nucleates 13-protofilament microtubules. Cryo-EM reconstructions of {gamma}-TuRC-capped microtubule minus-ends reveal the extensive intra- and inter-domain motions of {gamma}-TuRC subunits that accommodate its actin-containing luminal bridge and establish lateral and longitudinal interactions between {gamma}- and -tubulins. Our structures reveal how free {gamma}-TuRC, an inefficient nucleation template due to its splayed conformation, transforms into a stable cap that blocks addition or loss of /{beta}-tubulins from minus-ends and sets the lattice architecture of cellular microtubules.