Inhibition of SF3B1 affects recruitment of P-TEFb to chromatin through multiple mechanisms
Inhibition of SF3B1 affects recruitment of P-TEFb to chromatin through multiple mechanisms
Ansa, G.; Murphy, S.; Tellier, M.
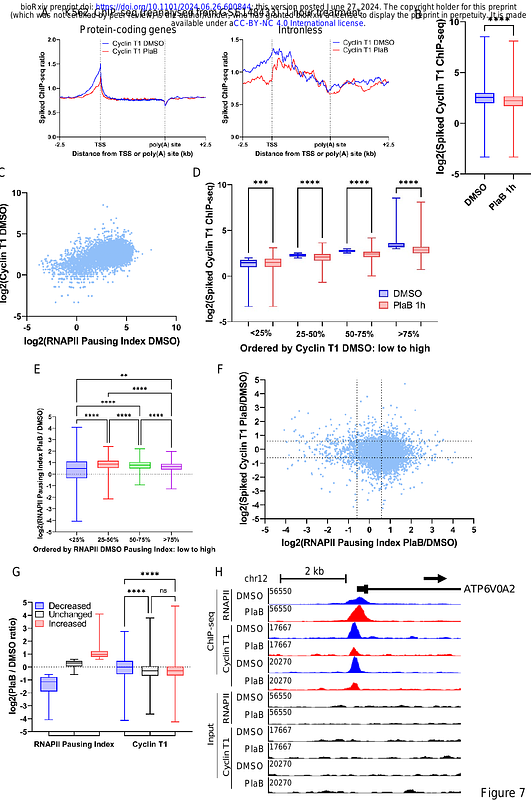
AbstractProcessing of nascent pre-mRNAs is tightly coupled to transcription by RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) through reversible phosphorylation of the polymerase and associated factors by transcriptional kinases. P-TEFb, comprising cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)9 and cyclin T1, is a key transcription elongation kinase, which also regulates co-transcriptional splicing and mRNA cleavage and polyadenylation. Chemical inhibition of SF3B1, a component of the splicing factor U2 snRNP, decreases P-TEFb recruitment to chromatin and mirrors the effect of P-TEFb inhibition on transcription. However, the mechanism of this effect of SF3B1 inhibitors was unclear. Here we show that SF3B1 inhibition causes rapid nuclear export of P-TEFb and loss of SF3B1 phosphorylation. SF3B1 is in complex with P-TEFb on chromatin with the elongation/splicing factor HTATSF1 and the splicing factor SNW1. SF3B1 inhibition causes the nuclear export of SNW1, but not of HTATSF1. The chromatin association of AFF4, an interaction partner of P-TEFb, is also affected by SF3B1 inhibition. Surprisingly, SF3B1 inhibition promotes degradation of SRSF2, a splicing factor known to help recruit P-TEFb to chromatin. Our results indicate that SF3B1 inhibition affects P-TEFb recruitment to genes via multiple pathways. Together, these interactions ensure efficient coupling of transcription and splicing.


