TREVI: A Transcriptional Regulation-driven Variational Inference Model to Speculate Gene Expression Mechanism with Integration of Single-cell Multi-omics
TREVI: A Transcriptional Regulation-driven Variational Inference Model to Speculate Gene Expression Mechanism with Integration of Single-cell Multi-omics
Cao, L.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, F.; Wang, Y.
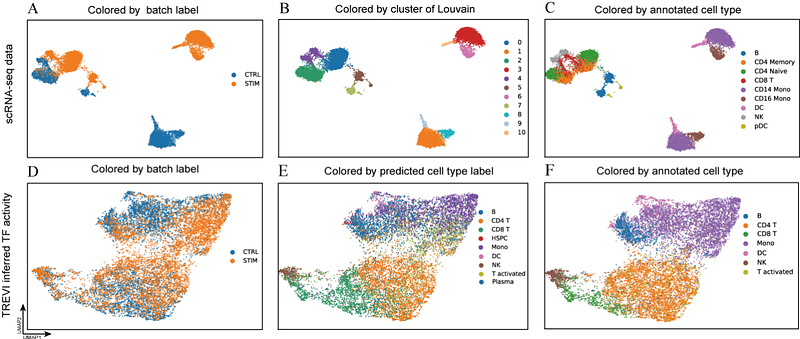
AbstractSingle-cell multi-omics technology enables the concurrent measurement of multiple molecular entities, making it critical for unraveling the inherent gene regulation mechanisms driving cell heterogeneity. However, existing multi-omics techniques have limitations in capturing the intricate regulatory interactions among these molecular components. In this study, we introduce TREVI(Transcriptional REgulation-driven Variational Inference), a novel method that integrates the well-established gene regulation structure with scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq data through an advanced Bayesian framework. TREVI models the generation of gene expression profiles in individual cells by considering the integrated influence of three fundamental biological factors: accessibility of cis-regulatory elements regions, transcription factor (TF) activities and regulatory weights. TF activities and regulatory weights are probabilistically represented as latent variables, which capture the inherent gene regulatory significance. Hence, in contrast to gene expression, TF activities and regulatory weights that depict the cell states from a more intrinsic perspective, can keep consistent across diverse datasets. TREVI exhibits superior performance when compared to baseline methods in a variety of biological analyses, including cell typing, cell development tracking, and batch effect correction, as validated through comprehensive benchmarking. Moreover, TREVI can reveal variations in TF-gene regulation relationships across cells. The pretrained TREVI model can work even when only scRNA-seq is available. Overall, TREVI introduces a pioneering biological-mechanism-driven framework for elucidating cell states at a gene regulatory level. The model\'s structure is adaptable for the inclusion of additional biological factors, allowing for flexible and more comprehensive gene regulation analysis.