Identification of novel therapeutic inhibitors against E6 and E7 oncogenes of HPV-16 associated with cervical cancer
Identification of novel therapeutic inhibitors against E6 and E7 oncogenes of HPV-16 associated with cervical cancer
Younas, S.; Malik, Z. I.; Khan, M. U.; Manzoor, S.; Hammad, H. M.; Rehman, H. M.; Akter, S.
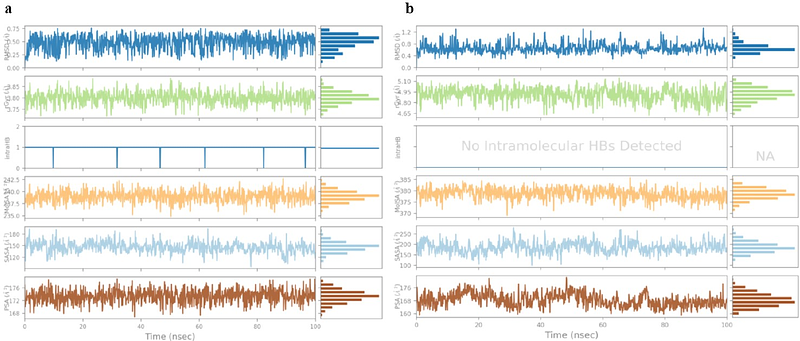
AbstractBackground: Human Papilloma Virus type 16 (HPV-16) is highly oncogenic with the E6 and E7 oncogenes playing crucial roles in the pathogenesis of HPV-related cervical carcinogenesis. Targeting these oncoproteins with specific inhibitors offers a promising approach for therapeutic intervention. Objective: This study aimed to identify potential inhibitors of the HPV-16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins through an in silico approach, providing a foundation for the development of targeted therapies against HPV associated malignancies. Methodology: We performed virtual screening on a library of 1000 compounds to identify promising candidates. Subsequent molecular docking studies were conducted to assess the binding affinities of the promising candidates. The top-scoring compounds for oncoproteins were then subjected to molecular dynamics simulations to evaluate their stability and interaction profiles. Results: The virtual screening identified 14 promising candidates followed by docking studies. Among these Galangin was identified as a promising inhibitor for the E6 oncogene, while Neoechinulin showed potential as an inhibitor of the E7 oncogene. Conclusion: Our findings suggest Galangin and Neoechinulin with high potential as therapeutic inhibitors of HPV-16 E6 and E7 oncogenes respectively. These inhibitors could contribute significantly to the development of targeted therapies against HPV associated malignancies. However, further in vitro and in vivo investigations are required to use these phytochemicals as antiviral agents against HPV-16.