The pyrethroid insecticide deltamethrin disrupts neuropeptide and monoamine signaling pathways in the gastrointestinal tract
The pyrethroid insecticide deltamethrin disrupts neuropeptide and monoamine signaling pathways in the gastrointestinal tract
White, A. C.; Krout, I. N.; Mouhi, S.; Chang, J.; Kelly, S. D.; Caudle, W. M.; Sampson, T.
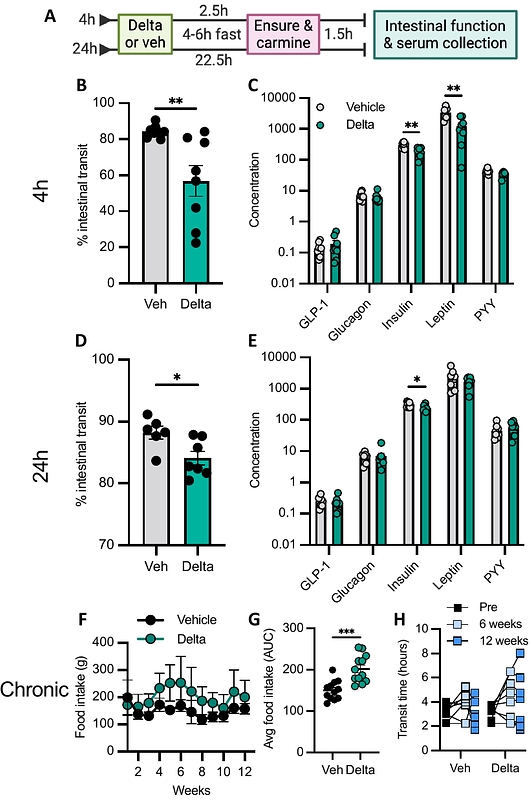
AbstractEnteroendocrine cells (EECs) are a rare cell type of the intestinal epithelium. Various subtypes of EECs produce distinct repertoires of monoamines and neuropeptides which modulate intestinal motility and other physiologies. EECs also possess neuron-like properties, suggesting a potential vulnerability to ingested environmental neurotoxicants. One such group of toxicants are pyrethroids, a class of prevalent insecticides used residentially and agriculturally. Pyrethroids agonize voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs), inducing neuronal excitotoxicity, and affect the function of monoamine-producing neurons. Given their anatomical location at the interface with the environment and their expression of VGSCs, EECs likely represent a vulnerable cell-type to oral pyrethroid exposure. In this study, we used the EEC cell line, STC-1 cells, to evaluate the effects of the common pyrethroid deltamethrin on the functional status of EECs. We find that deltamethrin impacts both expression of serotonergic pathways and inhibits the adrenergic-evoked release of an EEC hormone, GLP-1, in vitro. In a mouse model of oral exposure, we found that deltamethrin induced an acute, yet transient, loss of intestinal motility, in both fed and fasted conditions. This constipation phenotype was accompanied by a significant decrease in peripheral serotonin production and an inhibition of nutrient-evoked intestinal hormone release. Together, these data demonstrate that deltamethrin alters monoaminergic signaling pathways in EECs and regulates intestinal motility. This work demonstrates a mechanistic link between pyrethroid exposure and intestinal impacts relevant to pyrethroid-associated diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, neurodegenerative disease, and metabolic disorders.