Closure of the gamma-tubulin ring complex by CDK5RAP2 activates microtubule nucleation
Closure of the gamma-tubulin ring complex by CDK5RAP2 activates microtubule nucleation
Xu, Y.; Munoz-Hernandez, H.; Krutyholowa, R.; Marxer, F.; Cetin, F.; Wieczorek, M.
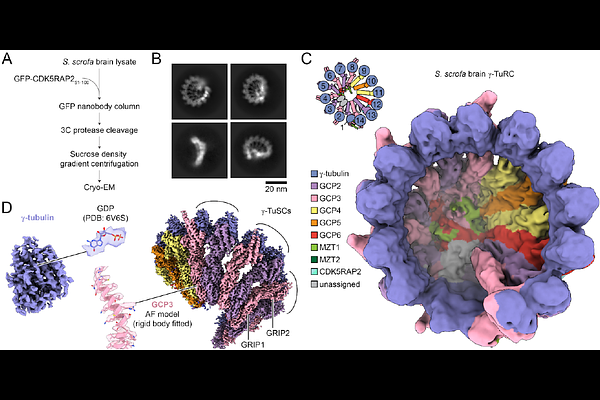
AbstractMicrotubule nucleation in cells is templated by the gamma-tubulin ring complex (gamma-TuRC), a 2.3 MDa multiprotein assembly concentrated at microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs). Current gamma-TuRC structures exhibit an open conformation that deviates from the geometry of alpha/beta-tubulin in the microtubule, potentially explaining their low in vitro microtubule-nucleating activity. Several proteins have been proposed to activate the gamma-TuRC, but the mechanisms underlying activation are not known. Here, we isolated the porcine gamma-TuRC using CDK5RAP2\'s centrosomin motif 1 (CM1) and determined its structure with cryo-electron microscopy. 3D heterogeneity analysis revealed an unexpected conformation of the gamma-TuRC, in which five protein modules containing MZT2, GCP2, and CDK5RAP2 decorate the outer face of the holocomplex. These decorations drive a long-range constriction of the gamma-tubulin ring, bringing the GCP2/GCP3-rich core of the complex in close agreement with the architecture of a microtubule. A purified CDK5RAP2 fragment stimulated the microtubule nucleating activity of the porcine gamma-TuRC as well as a reconstituted, CM1-free human complex in single molecule assays. Our results show that CDK5RAP2 activates the gamma-TuRC by promoting gamma-tubulin ring closure, providing a structural mechanism for the regulation of microtubule nucleation by CM1 motif proteins in mammals and revealing conformational transitions in gamma-tubulin that prime it for templating microtubule nucleation at MTOCs.