MAPK Phosphatase-5 is required for TGF-β signaling through a JNK-dependent pathway
MAPK Phosphatase-5 is required for TGF-β signaling through a JNK-dependent pathway
Dorry, S. J.; Perla, S.; Bennett, A. M.
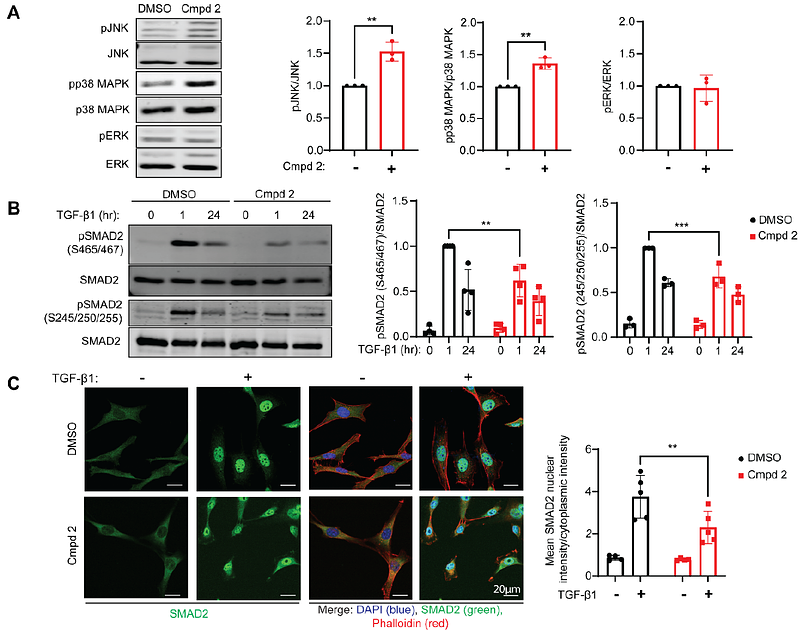
AbstractMitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatases (MKPs) constitute members of the dual-specificity family of protein phosphatases that dephosphorylate the MAPKs. MKP-5 dephosphorylates the stress-responsive MAPKs, p38 MAPK and JNK, and has been shown to promote tissue fibrosis. Here, we provide insight into how MKP-5 regulates the transforming growth factor-{beta} (TGF-{beta}) pathway, a well-established driver of fibrosis. We show that MKP-5-deficient fibroblasts in response to TGF-{beta} are impaired in SMAD2 phosphorylation at canonical and non-canonical sites, nuclear translocation, and transcriptional activation of fibrogenic genes. Consistent with this, pharmacological inhibition of MKP-5 is sufficient to block TGF-{beta} signaling, and that this regulation occurs through a JNK-dependent pathway. By utilizing RNA sequencing and transcriptomic analysis, we identify TGF-{beta} signaling activators regulated by MKP-5 in a JNK-dependent manner, providing mechanistic insight into how MKP-5 promotes TGF-{beta} signaling. This study elucidates a novel mechanism whereby MKP-5-mediated JNK inactivation is required for TGF-{beta} signaling and provides insight into the role of MKP-5 in fibrosis.


