Structural insights into the remodeled RNA polymerase II complex on an RNA template
Structural insights into the remodeled RNA polymerase II complex on an RNA template
Hao, J.; Qin, Z.; Ma, J.; Qu, J.; Wang, Y.; Folimonova, S. Y.; Liu, B.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.
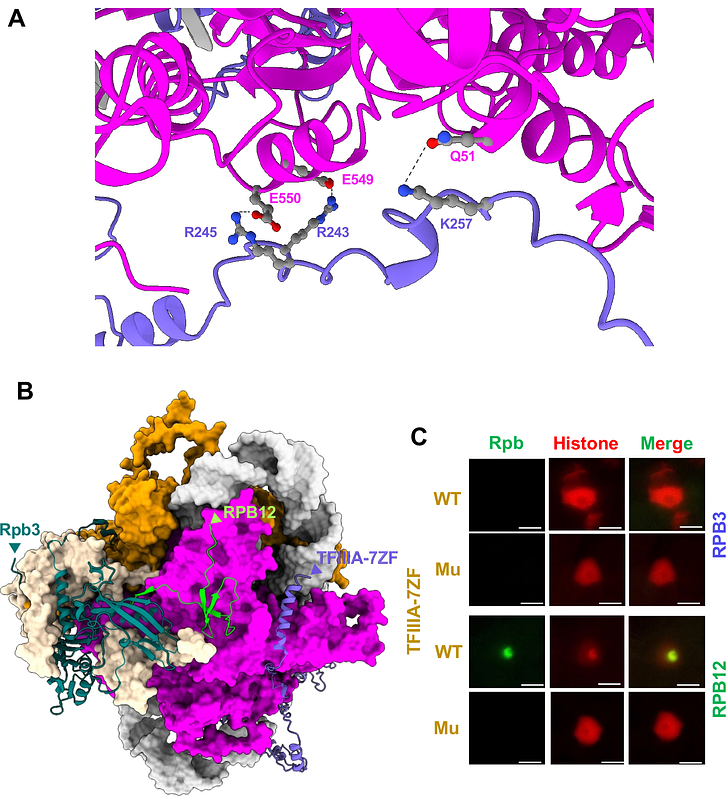
AbstractDNA-dependent RNA polymerases recognize not only DNA but also RNA templates. This RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity was exploited by human hepatitis delta virus in mammalian cells and viroids in plants. Emerging evidence infers a re-organization of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription complex on potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd) RNA template, an understudied layer of transcriptional regulation. Here, we provide evidence confirming that the reorganization of the 12-subunit Pol II to 7-subunit occurs in vivo for PSTVd transcription. Rpb4, Rpb5, Rpb6, Rpb7, and Rpb9 are not involved in PSTVd transcription. A splicing variant of the transcription factor IIIA with seven zinc finger domains (TFIIIA-7ZF) aids the remodeled Pol II in transcribing PSTVd. Based on AlphaFold3 prediction, we obtained the structure of the remodeled Pol II with PSTVd RNA and TFIIIA-7ZF. The predicted structure and experimental data both show that the N-terminus of TFIIIA-7ZF binds to the left terminal domain of PSTVd, while the C-terminus of TFIIIA-7ZF interacts with Rpb2. Altogether, the data illustrate an active form of heterogenous organization of the essential Pol II enzyme in vivo and provide structural insights into the remodeled Pol II and TFIIIA-7ZF transcription complex on RNA template.