Detection of rare plasmid hosts using a targeted Hi-C approach
Detection of rare plasmid hosts using a targeted Hi-C approach
Castaneda-Barba, S.; Ridenhour, B. J.; Top, E. M.; Stalder, T.
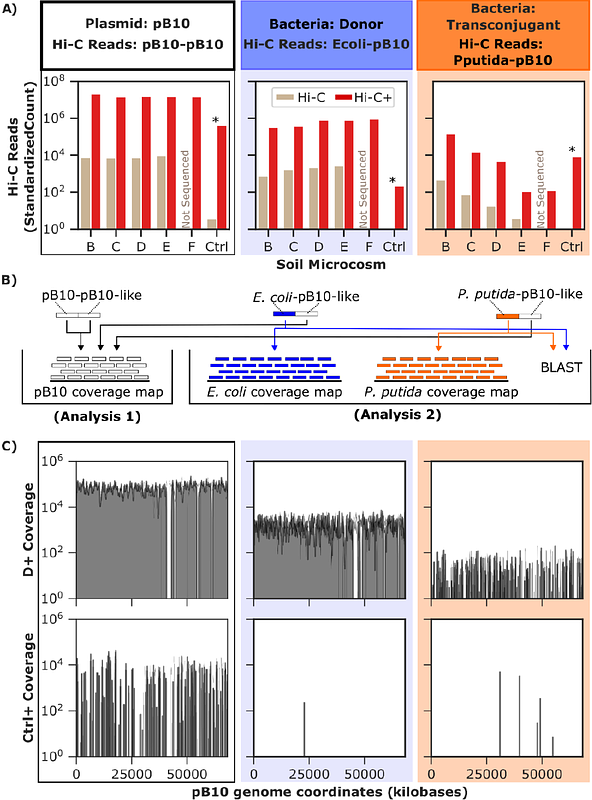
AbstractDespite the significant role plasmids play in microbial evolution, there is limited knowledge of their ecology, evolution, and transfer in microbial communities. Therefore, we developed and implemented a novel approach to identify rare plasmid hosts by combining Hi-C, a proximity ligation method, with enrichment for plasmid-specific DNA. We hereafter refer to this Hi-C enrichment approach as Hi-C+. Our experimental design mimicked scenarios in which the transfer of an antimicrobial resistance plasmid from a donor to a recipient in soil was increasingly rare. We established that Hi-C can link a plasmid to its host in soil when the relative abundance of that plasmid-host pair is as low as 0.001%. The Hi-C+ method further improved the detection limit of Hi-C 100-fold and allowed identification of plasmid hosts at the genus level. Therefore, Hi-C+ will facilitate the exploration of the ecological and evolutionary pathways that affect the spread of plasmids in natural environments.