Regenie.QRS: computationally efficient whole-genome quantile regression at biobank scale
Regenie.QRS: computationally efficient whole-genome quantile regression at biobank scale
Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Masala, M.; Fiorillo, E.; Devoto, M.; Cucca, F.; Ionita-Laza, I.
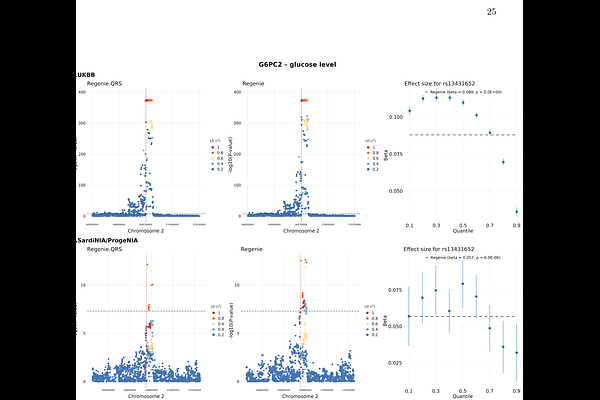
AbstractGenotype-phenotype associations can be context-dependent and dynamic in nature leading to heterogeneity of genetic effects across different parts of the phenotype distribution. Quantile regression, an alternative to linear regression for continuous phenotypes, is particularly well suited for detecting and characterizing heterogeneous genotype-phenotype associations. Here we propose a novel and computationally efficient whole-genome quantile regression technique, Regenie.QRS, for biobank-scale GWAS data with genetic structure. Our approach first estimates the polygenic effect, and then incorporates this effect as an offset in the non-mixed quantile regression model. Our simulations demonstrate robust control of type I error and higher power to detect heterogeneous associations relative to linear regression in GWAS, and improved power over the marginal quantile regression tests. We present applications using data from the UK Biobank and the ProgeNIA/SardiNIA project, where we show the advantages of Regenie.QRS in identifying and characterizing heterogeneous genetic effects. To cite just one interesting example, using quantile regression we are able to show that even though variants at the G6PC2 locus increase glucose levels, their effects are much stronger at lower quantiles of glucose level distribution than at higher quantiles, showing that G6PC2 serves as a guardian against low glucose levels without driving dangerous hyperglycemia, which may explain the lack of association with diabetes risk.