Dynamic co-expression modular network analysis of bHLH transcription factors regulation in the potato spindle tuber viroid-tomato pathosystem
Dynamic co-expression modular network analysis of bHLH transcription factors regulation in the potato spindle tuber viroid-tomato pathosystem
Avina-Padilla, K.; Zambada-Moreno, O.; Jimenez-Lima, M. A.; Hammond, R.; Hernandez-Rosales, M.
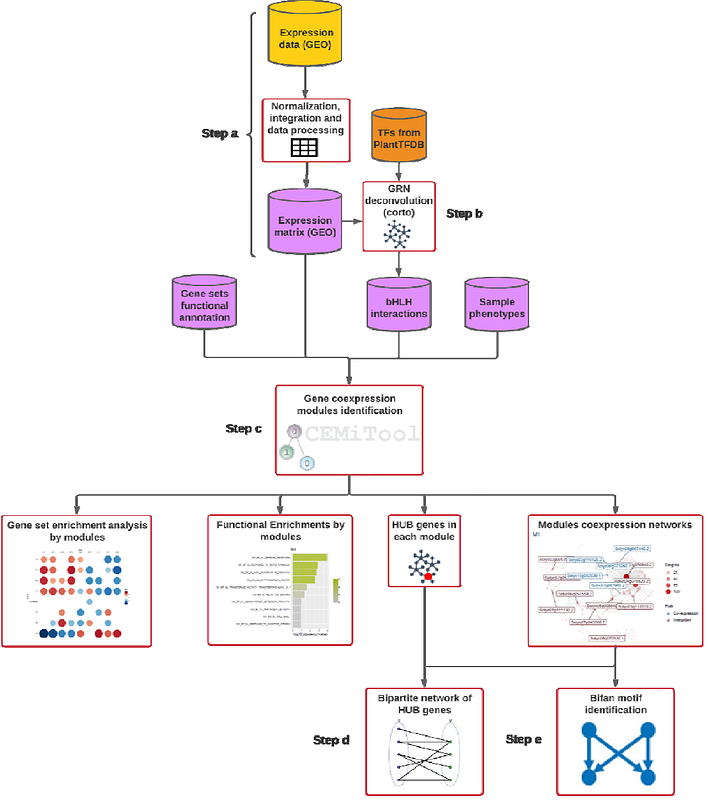
AbstractViroids, minimalist plant pathogens, present significant threats to crops by causing severe diseases. The use of high-throughput sequencing technologies for analyzing the transcriptomes of viroid-infected host plants has yielded informative information on gene regulation by these pathogens, however a complete understanding of the transcriptome data suffers from the inclusion of numerous genes of unknown function. Co-expression analysis addresses this by clustering genes into modules based on global gene expression levels. Our previous study emphasized basic helix-loop-helix protein (bHLH) transcriptional reprogramming in tomato in response to different potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd) strains. In the current research, we delve into tissue-specific gene modules, particularly in root and leaf tissues, governed by bHLH transcription factors during PSTVd infections. Utilizing public datasets that span Control (C; (mock-inoculated), PSTVd-mild (M), and PSTVd-severe (S23) strains in time-course infections, we uncovered differentially expressed gene modules. These modules were functionally characterized, identifying essential hub genes. We identified the roles of bHLH transcription factors (TFs) in managing processes like photosynthesis and rapid membrane repair in infected roots. In leaves, external layer alterations influenced photosynthesis, linking bHLH TFs to distinct metabolic functions. Expanding on these findings, we explored bipartite networks, discerning both common and unique bHLH TF regulatory roles, notably highlighting the bifan motif\'s significance in these interactions. Through this holistic approach, we deepen our understanding of viroid-host interactions and the intricate regulatory mechanisms underpinning them.