MoDorado: Enhanced detection of tRNA modifications in nanopore sequencing by off-label use of modification callers
MoDorado: Enhanced detection of tRNA modifications in nanopore sequencing by off-label use of modification callers
Rubsam, F.; Lui-Wei, W.; Sun, Y.; Patel, B. I.; van der Toorn, W.; Piechotta, M.; Dieterich, C.; von Kleist, M.; Ehrenhofer-Murray, A. E.
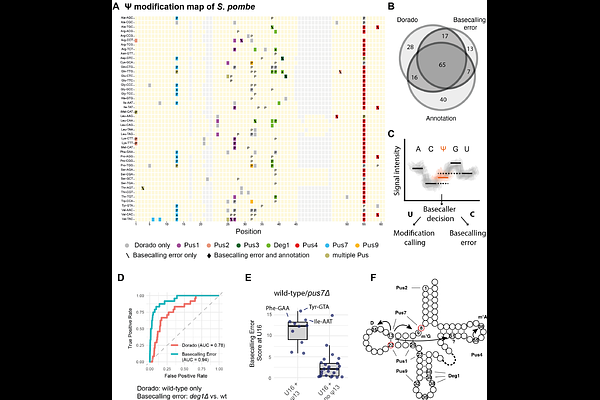
AbstractRapid and accurate identification of tRNA modifications is crucial for understanding their role in protein translation and disease. However, their detection on tRNAs is challenging due to their high modification density. Recently, modification calling models for nanopore direct RNA sequencing became available for pseudouridine ({Psi}), m6A, inosine and m5C, as part of the Dorado basecaller. Applying the {Psi} model to tRNAs, we have mapped both known and novel {Psi} sites in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and assigned the responsible pseudouridine synthetases. Furthermore, we have developed MoDorado, an algorithm to detect modifications beyond those used in model training (off-label use) by measuring prediction differences of pre-trained machine learning models. By leveraging the {Psi}/m6A/inosine/m5C models, MoDorado detected seven additional modifications (ncm5U, mcm5U, mcm5s2U, m7G, queuosine, m1A, and i6A), thus generating a tRNA modification map of S. pombe. This work demonstrates the potential of pre-trained models in determining the intricate landscape of tRNA modifications.