Hemodynamic Characteristics of Acute Hypersensitivity Reaction Induced by PEGylated Nanocomposite in Rats: Mechanism at the Nano-Bio Interface
Hemodynamic Characteristics of Acute Hypersensitivity Reaction Induced by PEGylated Nanocomposite in Rats: Mechanism at the Nano-Bio Interface
Ngo, S.-T.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, S.-Y.; Sun, M.-T.; Yu, J.-S.; Chien, K.-Y.; Chen, H.-M.; Ma, Y.-H.
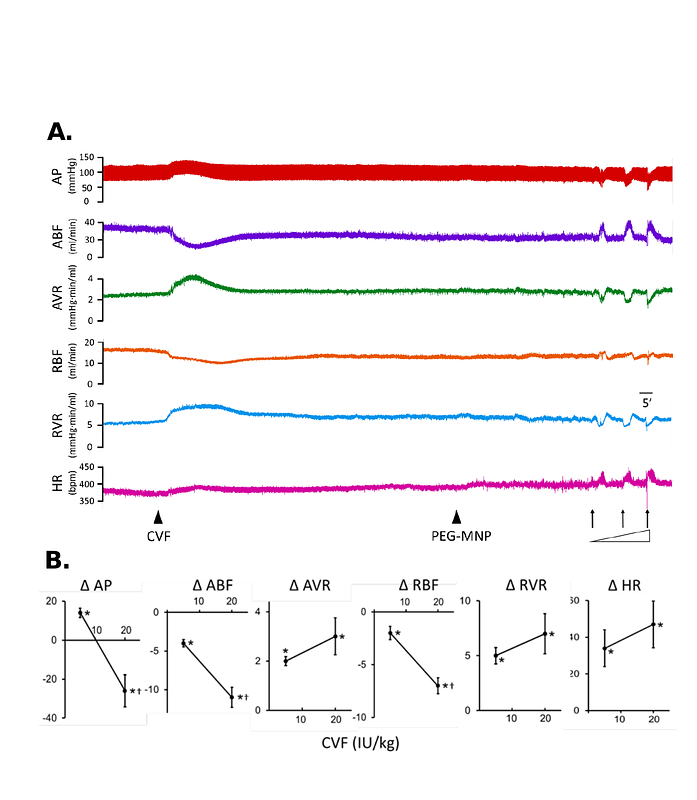
AbstractBackground: Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-modified nanocomposites may induce acute hypersensitivity reactions (HSR), including complement activation and hypotension, followed by tachyphylaxis with an unknown mechanism. We established a rodent model of HSR, and hypothesized that the formation of protein corona with a composition specific to PEGylated nanoparticles induces an acute and transient microvascular occlusion that entrains the hemodynamic effects. Methods: Hemodynamic parameters of renal and cremaster vasculature were measured in anesthetized rats using ultrasonic flowmetry and laser speckle contrast imaging, respectively. Proteomic analysis on the hard corona of dextran-coated magnetic nanoparticles (MNP) with and without PEGylation was conducted after incubation of the nanoparticles with plasma from rats. Results: PEG-MNP iv. induced a temporary reduction by approximately 30 mmHg in arterial pressure, with significant reduction in renal/cremaster blood flow and cardiac output, followed by tachyphylaxis and thrombocytopenia. PEG-MNP, but not pristine MNP, significantly increased renal vascular resistance with a reduction in the calculated cross-sectional area of renal vessels, suggesting microvascular occlusion. In contrast, the vasodilator acetylcholine decreased both blood pressure and vascular resistance before and after administration of PEG-MNP, suggesting an intact endothelium. Complement depletion by cobra venom factor induced a transient reduction in blood flow and prevented PEG-MNP-induced hemodynamic effects, suggesting an important role of complement activation. Proteomic analysis identified much higher complement proteins in the hard corona of PEG-MNP vs. MNP in plasma from rats; preexposure of rats to PEG-MNP or MNP in vivo greatly reduced plasma proteins with high affinity for PEG-MNP. The results suggest that complement depletion may mediate tachyphylaxis in response to the 2nd dose of PEG-MNP. Conclusion: PEGylated nanocomposites-induced complement activation in the protein corona may trigger the hemodynamic effects and subsequent pathophysiological responses in HSR of rats.