PG-SCUnK: measuring pangenome graph representativeness using Single-Copy and Universal K-mers
PG-SCUnK: measuring pangenome graph representativeness using Single-Copy and Universal K-mers
Cumer, T.; Milia, S.; Leonard, A. S.; Pausch, H.
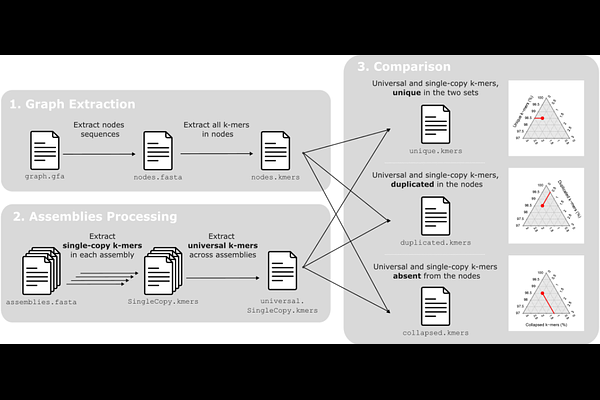
AbstractMotivation: Pangenome graphs integrate multiple assemblies to represent non-redundant genetic diversity. However, current evaluations of pangenome graph quality rely primarily on technical parameters (e.g., total length, number of nodes/edges, growth curves), which fail to assess how effectively the graph represents homologous stretches across the integrated assemblies. Results: We introduce a novel method to quantitatively assess how well a pangenome graph represents its integrated assemblies. Our method quantifies how many single-copy and universal k-mers (SCUnK) from the source assemblies are uniquely and completely represented within the graph nodes. Implemented in the open-source tool PG-SCUnK, this approach identifies the fractions of unique, duplicated, and collapsed k-mers, which correlate with short read mapping rates to the pangenome graph. Insights provided by PG-SCUnK facilitate the selection of appropriate parameters to build optimal pangenome graphs. Availability and implementation: A bash implementation of the PG-SCUnK workflow is freely available under the GNU GPLv3 license at https://github.com/cumtr/PG-SCUnK/.