Effective Markovian dynamics method of solving non-Markovian dynamics of stochastic gene expression
Effective Markovian dynamics method of solving non-Markovian dynamics of stochastic gene expression
Li, Y.; Jia, C.
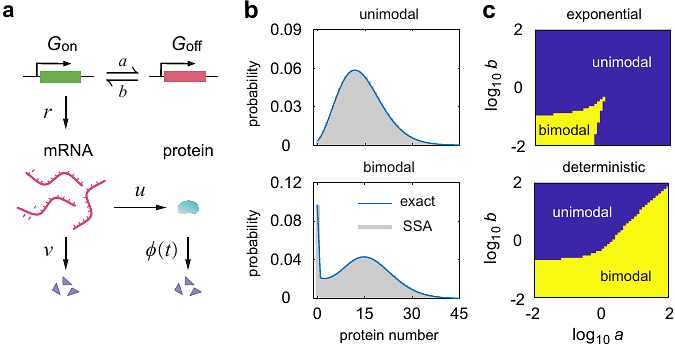
AbstractExperiments have shown that over 10% of proteins are degraded non-exponentially. Gene expression models for non-exponentially degraded proteins are notoriously difficult to solve since the underlying stochastic dynamics is non-Markovian. Here we develop an effective Markovian dynamics (EMD) method which converts a large class of non-Markovian models into effective Markovian ones so that they have the same mRNA and protein distributions at any fixed time. Using the EMD approach, we analytically solve some classical gene expression models with non-exponential or delayed protein decay, whose exact distributions are previously unknown and fail to be obtained using conventional queueing theory. Our theory successfully explains why non-exponentially degraded proteins on average have smaller mRNA-protein correlation than exponentially degraded proteins, and it predicts that bimodality is significantly enhanced in the presence of delayed protein degradation.