BRD4 binds the nucleosome via both histone and DNA interactions
BRD4 binds the nucleosome via both histone and DNA interactions
Zhu, J.; Leith, E. M.; O'Donnell, E. N.; Manzano, B. P.; Wu, S.-Y.; Chiang, C.-M.; Armache, J.-P.; Tan, S.
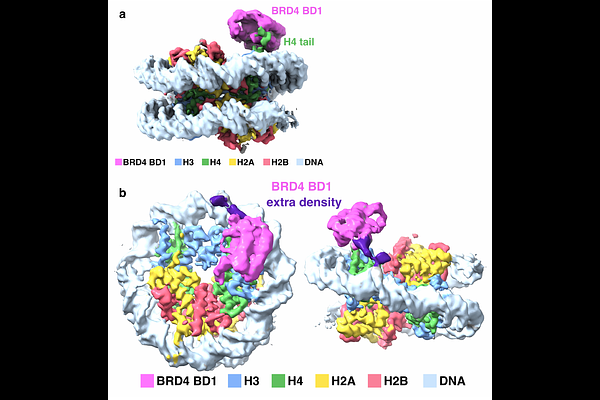
AbstractBRD4, a bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) family transcriptional regulator of cell cycle progression, cell differentiation and cancer development, is believed to be recruited to chromatin via interactions between its tandem bromodomains (BD1 and BD2) and acetylated histone tails. Although extensive studies have explained how individual BRD4 bromodomains bind to acetylated peptides and how BET inhibitors interfere with such interactions, equivalent studies of full-length BRD4 protein with the nucleosome have been lacking. Our cryo-EM structure of the BRD4 short (BRD4-S) isoform bound to a nucleosome diacetylated on histone H4 shows how BRD4 BD1 engages both the H4 tail and nucleosomal DNA. Unexpectedly, our biochemical studies indicate that BRD4 uses basic regions outside of the bromodomains to bind nucleosomes tightly even in the absence of histone acetylation. Our results further show that histone H4 acetylation influences the conformation of the BRD4/nucleosome complex.