End-product inhibition of the LRRK2-counteracting PPM1H phosphatase
End-product inhibition of the LRRK2-counteracting PPM1H phosphatase
Adhikari, A.; Tripathi, A.; Chiang, C. Y.; Sherpa, P. L.; Pfeffer, S. R.
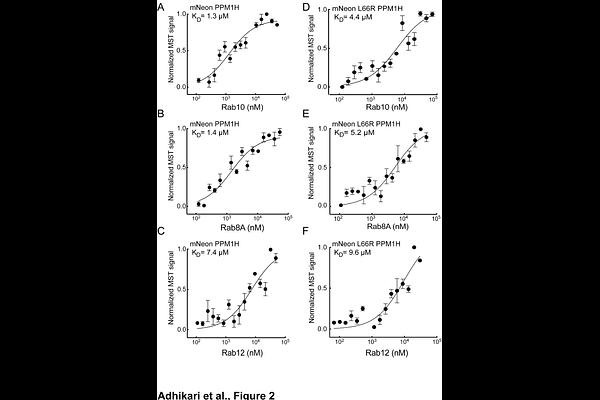
AbstractPPM1H phosphatase reverses Parkinson disease-associated, Leucine Rich Repeat Kinase 2-mediated, Rab GTPase phosphorylation. We showed previously that PPM1H relies on an N-terminal amphipathic helix for Golgi membrane localization and this helix enables PPM1H to associate with liposomes in vitro; binding to highly curved liposomes activates PPM1H phosphatase activity. We show here that PPM1H also contains an allosteric binding site for its non-phosphorylated reaction products, Rab8A and Rab10. Microscale thermophoresis revealed that PPM1H binds thio-phosphorylated Rab8A at the active site with a KD of about 1 micromolar; binding of Rab8A and Rab10 to an alternative site is of similar affinity and is not detected for another LRRK2 substrate, Rab12. Non-phosphorylated Rab8A or Rab10 inhibit PPM1H phosphatase reactions at concentrations consistent with their measured binding affinities and fail to inhibit PPM1H L66R phosphatase reactions. Independent confirmation of non-phosphorylated Rab binding to PPM1H was obtained by sucrose gradient co-flotation of non-phosphorylated Rabs with liposome-bound PPM1H. Finally, Rab8A or Rab10 binding also requires PPM1Hs amphipathic helix, without which the interaction affinity is decreased about 6-fold. These experiments indicate that Golgi associated Rab proteins contribute to the localization of PPM1H and non-phosphorylated Rabs regulate PPM1H phosphatase activity via an allosteric site. Targeting this site could represent a strategy to enhance PPM1H-mediated dephosphorylation of LRRK2 substrates, offering a potential therapeutic approach to counteract LRRK2-driven Parkinson disease.