STmiR: A Novel XGBoost-Based Framework for Spatially Resolved miRNA Activity Prediction
STmiR: A Novel XGBoost-Based Framework for Spatially Resolved miRNA Activity Prediction
Yuan, J.; Xu, P.; Liu, W.; Ye, Z.
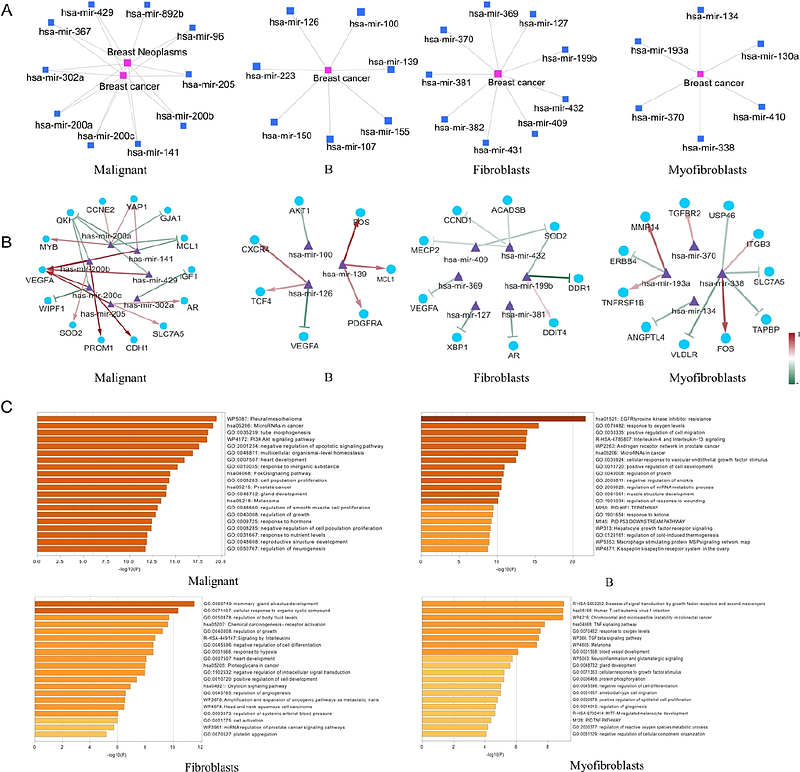
AbstractMicroRNAs (miRNAs) are critical regulators of gene expression in cancer biology; however, their spatial dynamics within tumor microenvironments (TME) remain underexplored owing to technical limitations in current spatial transcriptomics (ST) technologies. To address this gap, we present STmiR, a novel XGBoost-based framework for spatially resolved miRNA activity predictions. STmiR integrates bulk RNA-seq data (TCGA and CCLE) with spatial transcriptomics profiles to model nonlinear miRNA-mRNA interactions, achieving a high predictive accuracy (Spearmans {rho} > 0.8) across four major cancer types (breast, lung, ovarian, and prostate). Applied to 10X Visium ST datasets from nine cancers, STmiR identified six pan-cancer conserved miRNAs (e.g., hsa-miR-21, hsa-let-7a) consistently ranked in the top 40 across malignancies, and uncovered cell-type-specific regulatory networks in fibroblasts, B cells, and malignant cells. A breast cancer case study validated the utility of STmiR by linking miR-205 to androgen receptor (AR) signaling and miR-200b to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). By enabling the spatial mapping of miRNA activity, STmiR provides a transformative tool to dissect miRNA-mediated regulatory mechanisms in cancer progression and TME remodeling, with implications for biomarker discovery and precision oncology.