Caspase-8 is a novel modulator of Homologous Recombination Repair in response to ionizing radiations
Caspase-8 is a novel modulator of Homologous Recombination Repair in response to ionizing radiations
Barila, D.; Contadini, C.; Ferri, A.; Di Girolamo, C.; Cirotti, C.; Fiscon, G.; Paci, P.; Marzullo, M.; Gentileschi, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Strauss, R.; Del Bufalo, D.; Ciapponi, L.
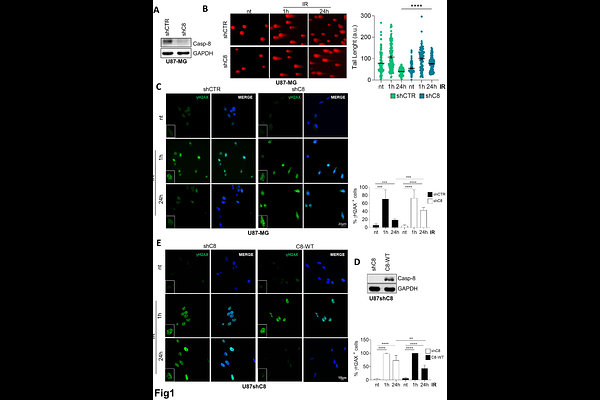
AbstractCaspase-8 is a cysteine protease historically regarded as anti-neoplastic protein, thanks to its role in apoptosis. However, Caspase-8 expression is retained or even enhanced in several tumors, including glioblastoma (GBM), where it plays pro-tumor functions. We previously reported that it is a negative prognostic factor and contributes to resistance against DNA damaging agents, such as ionizing radiations (IR) and Temozolomide, commonly used in standard GBM treatment. We therefore investigated whether Caspase-8 may sustain DNA repair pathways proficiency in GBM. Here we uncover a novel role of Caspase-8 as promoter of the Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR). Importantly, IR promote Caspase-8 transient nuclear translocation and its recruitment to the chromatin. Moreover, Caspase-8 sustains the expression and the recruitment to the chromatin upon IR of RAD51 and CtIP, two key players of the HRR. Consistently, we identify a synthetically lethal interaction between Caspase-8 and PARP inhibition, that may ameliorate GBM response to IR. Remarkably, by using Caspase-8-/- murine embryo fibroblasts and a Drosophila melanogaster Caspase-8 mutant, we demonstrate that Caspase-8 plays an evolutionary conserved role in DNA repair.