Small molecule inhibition of CPSF3 impacts R-loop distribution
Small molecule inhibition of CPSF3 impacts R-loop distribution
Corey, D. R.; Hu, J.; Hofman, C.; Tse, V.
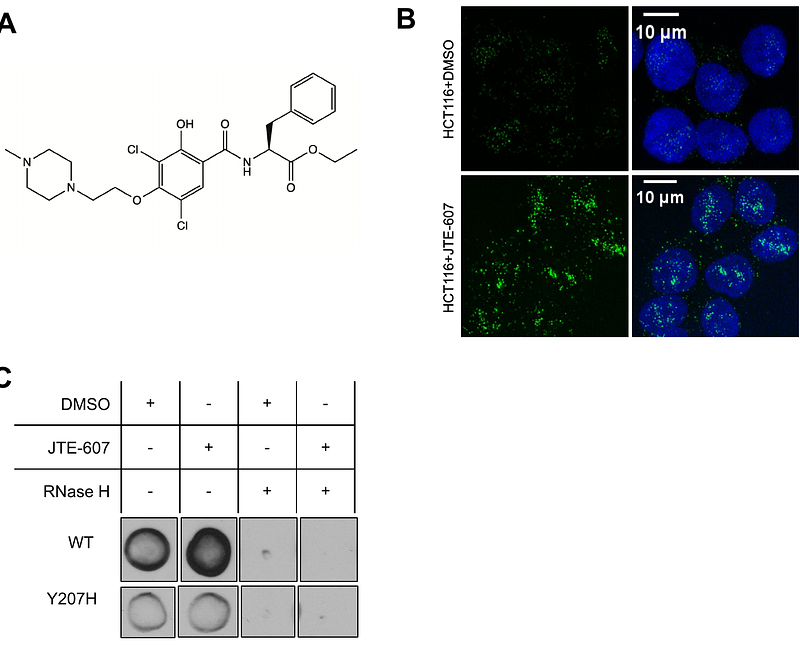
AbstractR-loops are three-stranded nucleic acid structures consisting of an RNA/DNA hybrid and a displaced strand of DNA. These structures have been implicated in a variety of regulatory cellular processes. Their untimed or excess accumulation, however, can cause genomic instability and induce DNA damage. Most R-loops form co-transcriptionally when the nascent transcript reanneals to unwound DNA duplex. Changes in the rate of transcription have the potential to impact R-loop formation, and compounds that modulate R-loop formation would be useful molecular tools and therapeutic leads. Cleavage and Polyadenylation Specific Factor 3 (CPSF3) recognizes the pre-mRNA 3\' cleavage site, cleaves the transcript prior to polyadenylation, and has been linked to R-loop formation. Inhibition of CPSF3 has been found to induce transcriptional readthrough and cell proliferation defects. A previous report suggested that inhibition of CPSF3 with a small molecule causes a global increase in R-loop abundance. Here we test the impact of YT-II-100, a novel inhibitor of CPSF3. We find that addition of YT-II-100 increases global R-loop formation but does not change R-loop formation at specific genes that are normally used as positive controls for R-loop formation. We performed parallel assays using previously reported compound JTE-607 and observed similar results. Our data emphasize the need for cautious interpretation of experiments using JTE-607 and YT-II-100. There may be different mechanisms of R-loop formation depending on gene loci, with the control of R-loop formation at some genes diverging from the regulation of global R-loop formation.