Drivers of spatio-temporal variability in a marine foundation species
Drivers of spatio-temporal variability in a marine foundation species
Giraldo-Ospina, A.; Bell, T.; Carr, M.; Caselle, J.
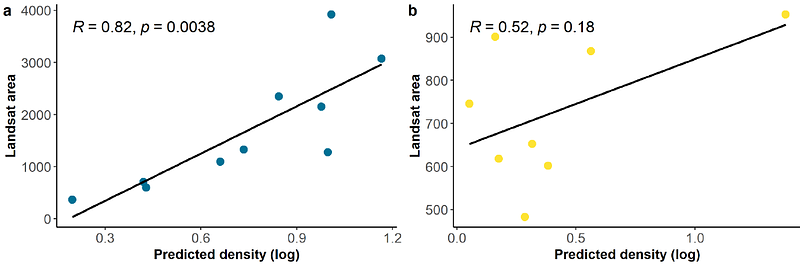
AbstractMarine foundation species are critical for the structure and functioning of ecosystems and constitute the pillar of trophic chains while also providing a variety of ecosystem services. In recent decades many foundation species have declined in abundance, sometimes threatening their current geographical distribution. Kelps (Laminariales) are the primary foundation species in temperate coastal systems worldwide. Kelp ecosystems are notoriously variable and identifying the key factors that control the dynamics of kelp abundance is key to predicting the fate of kelp ecosystems under climatic change and informing management and conservation decisions such as forest restoration. Here, we used in situ data from long-term monitoring programs across 1,350 km of coast spanning multiple biogeographic regions in the state of California (USA) to identify the major regional drivers of density of two dominant canopy-forming kelp species and to elucidate the spatial and temporal scales over which they operate. We used generalized additive models to identify the key drivers of density of two dominant kelp species (Nereocystis luetkeana and Macrocystis pyrifera) across four ecological regions of the state of California (north, central, south-west and south-east) and for the past two decades (2004-2021). Our study identified that the dominant drivers of kelp density varied between regions and species but always included some combination of nitrate availability, wave energy and exposure, density of purple sea urchins, and temperature as the most important predictors explaining 63% of the variability of bull kelp in the north and central regions, and 45% and 51.4% of the variability in giant kelp for the central/south-west and south-east regions, respectively. These large-scale analyses infer that a combination of lower nutrient availability, changes in wave energy and exposure, and increases in temperature and purple sea urchin counts have contributed to the decline of kelp observed in the last decade. Understanding the drivers of kelp dynamics can be used to identify regions and periods of significant change and historical stability, ultimately informing resource management and conservation decisions such as site selection for kelp protection and restoration.


