ODFormer: a Virtual Organoid for Predicting Personalized Therapeutic Responses in Pancreatic Cancer
ODFormer: a Virtual Organoid for Predicting Personalized Therapeutic Responses in Pancreatic Cancer
Xu, J.; Yang, X.; LI, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.; Guo, S.; Zou, J.; Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, C.; Li, P.; Jing, W.; Zheng, K.; Wu, X.; Gao, D.; Chen, L.; Jin, G.
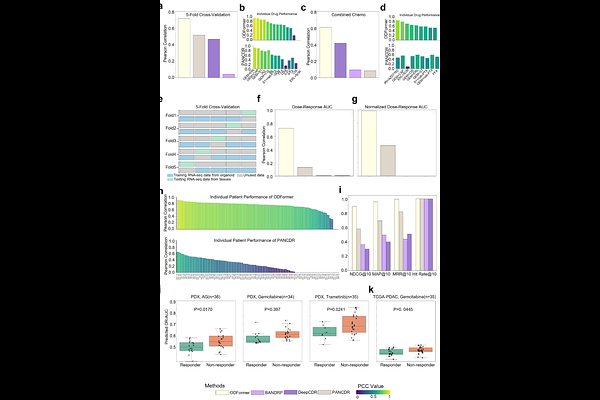
AbstractPancreatic cancer (PC) patient-derived organoids (PDOs) faithfully recapitulate therapeutic re-sponses but face clinical translation barriers, including high costs and technical complexity. To address these problems and the lack of frameworks for PDO based drug response assays, we developed ODFormer, a computational framework that simulates PC PDOs to predict clinically actionable, patient specific drug responses by integrating transcriptomic and mutational profiles. ODFormer first employed two encoders, pretrained on 30,000 pan cancer bulk transcriptomics and 1 million PC single cell profiles respectively, to distil tissue and organoid specific representations. Then, trained on our curated 14,000 PDO drug-response assay (across 183 PDOs and 98 drugs) us-ing a transformer augmented hybrid contrastive network, ODFormer significantly outperformed SOTA methods, notably achieving a PCC >0.9 in predicting standardized drug response. Multi-cohort retrospective analyses further demonstrated that ODFormer-guided personalized therapy significantly improves clinical outcomes, without requiring physical organoid assays. Fur-thermore, ODFormer identified novel PC subtypes with distinct therapeutic vulnerabilities and un-covered resistance biomarkers through analysis of predicted responders/non-responders. These were validated using independent datasets including TCGA PDAC. Notably, ODFormer guided treatment efficacy showed high concordance with prospective clinical responses by CA19-9.