When does additional information improve accuracy of RNA secondary structure prediction?
When does additional information improve accuracy of RNA secondary structure prediction?
Rose, L.; Giraldo, L. S.; Nguyen, D. D.; Wheeler, M.; Murrugarra, D.
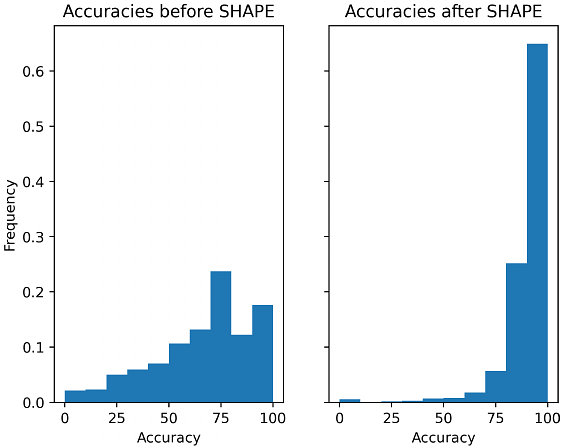
AbstractThe secondary structure of an RNA sequence plays an important role in determining its function, and accurate prediction of the structure is still a major goal in computational biology. Improvements in the prediction accuracy of the secondary structure can be achieved via auxiliary information. In this paper, we study features based on suboptimal formations competing with the minimum-free energy formation and investigate their role in determining the improvement of accuracy via auxiliary information, which we call directability. Here, we introduce a similarity measure among competing substructures called profiles. Then, we present an n-dimensional representation of the profiles which allows the use of topological data analysis (i.e., persistence landscapes) to obtain different metrics that represent topological features. Then, we built random forest classifiers using these novel features. We show how the similarity feature is more important for classifiers trained on sequences with similar structures while the topological features are more important for classifiers trained on sequences with dissimilar structures. We performed extensive testing on two sets of RNA sequences where we studied the sensitivity of the classification accuracy and their feature importance.