Ubiquitin-specific protease 8 controls B cell proteostasis and cell survival in multiple myeloma
Ubiquitin-specific protease 8 controls B cell proteostasis and cell survival in multiple myeloma
Dufner, A.; Thery, F.; Monaco, G.; Lazarevic, J. L.; Gorka, O.; Chevalier, N.; Frosch, M.; van der Heden van Noort, G. J.; Prinz, M.; Gross, O.; Geurink, P. P.; Schamel, W. W.; Heissmeyer, V.; Denzel, M. S.; Bruns, H.; Schemionek, M.; Impens, F.; Knobeloch, K.-P.
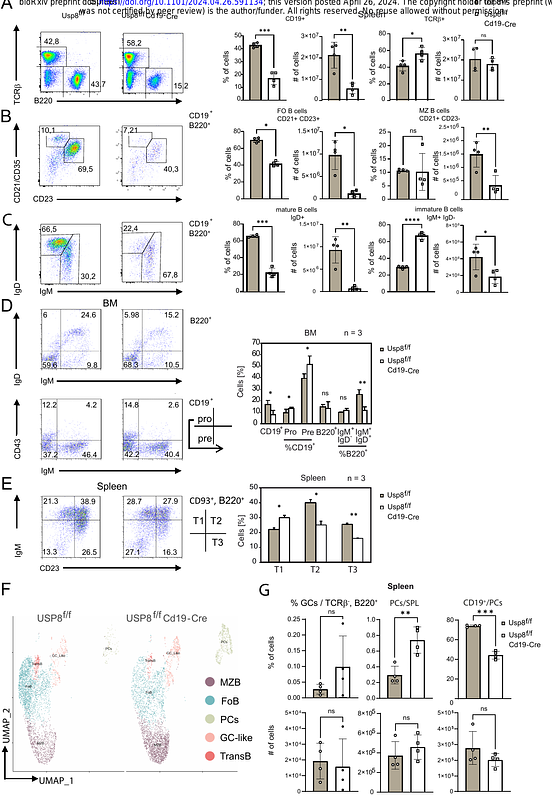
AbstractUbiquitin-specific protease 8 exerts multiple cellular functions and was identified as a potential target in a multiple myeloma vulnerability screen. Here we characterized the function of USP8 in B cells and multiple myeloma, and analyzed its impact on the global and ubiquitin-modified proteome. Usp8 deletion in mice starting at the the pre-B cell stage caused a partial block in B cell development favoring immature and innate-like B cells, as well as germinal center and plasma cells. This was accompanied by elevated immune-responses and Roquin depletion. Accordingly, correlation analyses in multiple myeloma patients revealed that low USP8 expression at diagnosis correlates with decreased survival. B cells expressing catalytically inactive USP8 accumulate protein modified with mixed ubiquitin/NEDD8 chains as hallmarks of proteotoxic stress, which we identified as favored USP8 substrates. USP8 knockdown reduced survival of bortezomib-resistant multiple myeloma cells in a lysosomal dysfunction-dependent manner. In contrast, the inhibitor DUB-IN-2 resensitized bortezomib-resistant multiple myeloma cells to treatment in a bortezomib-synergistic manner. Hence, our analyses uncovered the therapeutic potential of USP8 inhibition and of DUB-IN-2 in multiple myeloma.
