Genomic transfers help to decipher the ancient evolution of filoviruses and interactions with vertebrate hosts
Genomic transfers help to decipher the ancient evolution of filoviruses and interactions with vertebrate hosts
Taylor, D. J.; Barnhart, M. H.
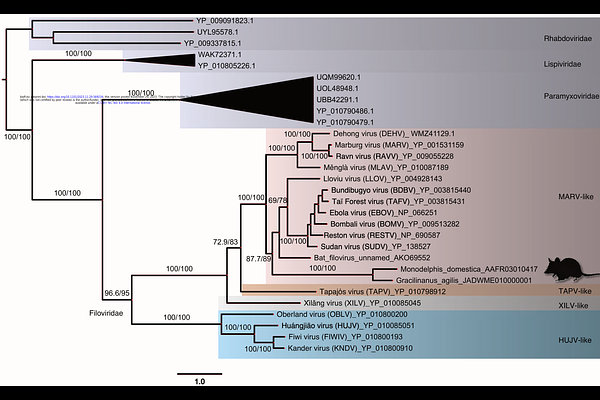
AbstractAlthough several filoviruses are dangerous human pathogens, there is conflicting evidence regarding their origins and interactions with animal hosts. Here we attempt to improve this understanding using the paleoviral record over a geological time scale, protein structure predictions, tests for evolutionary maintenance, and phylogenetic methods that alleviate sources of bias and error. We found evidence for long branch attraction bias in the L gene tree for filoviruses, and that using codon-specific models and protein structural comparisons of paleoviruses ameliorated conflict and bias. We found evidence for four ancient filoviral groups, each with extant viruses and paleoviruses with open reading frames. Furthermore, we found evidence of repeated transfers of filovirus-like elements to mouse-like rodents. A filovirus-like nucleoprotein ortholog with an open reading frame was detected in three subfamilies of spalacid rodents (present since the Miocene). These elements were unique among the detected filovirus-like paleoviruses in possessing open reading frames, expression products, and evidence for purifying selection. Our finding of structural conservation over geological time for paleoviruses informs virus and paleovirus discovery methods. Our results resolve a deep conflict in the evolutionary framework for filoviruses and reveal that genomic transfers to vertebrate hosts with potentially functional co-options have been more widespread than previously appreciated.