A new map of South Manchurian mixed forests facilitates the estimation of their area for conservation purposes
A new map of South Manchurian mixed forests facilitates the estimation of their area for conservation purposes
Dzizyurova, V.; Dudov, S.; Petrenko, T.; Krestov, P.; Grishchenko, M.; Korznikov, K.
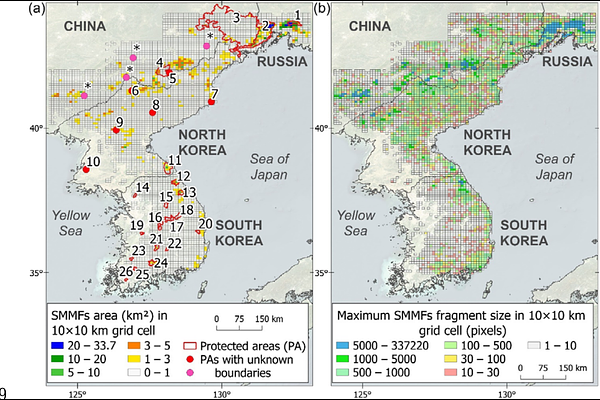
AbstractAbstract Questions: South Manchurian mixed forests (SMMFs) are among the most species-rich forest ecosystems in the world\'s temperate zone. These forests are experiencing significant degradation and have largely been replaced by secondary forests or agricultural lands and anthropogenic non-forest vegetation. A precise quantitative assessment of the remaining forest area is crucial due to their high conservation value. This study aims to assess the current area of these forests and evaluate changes over a historical period. Location: Korean Peninsula, northeastern China, and southern Primorsky Krai in Russia. Methods: We used the original SMMFs distribution dataset, including vegetation releves, literature on the distribution of these forests, and regional small-scale maps, to create a training set for classifying satellite data. We used Landsat Analysis Ready Data (1997-2001 and 2017-2021) as the basis for mapping. Mapping accuracy and area were estimated using a random stratified sampling, and forest changes were evaluated. Original releves and literature sources were used to verify SMMFs distribution. Results: The total area of SMMFs was estimated at 2,791.5 +- 1,496.2 km2, with significant uncertainty due to limited data from North Korea. Our results indicate that 45% of SMMFs are located in North Korea, 32% in Russia, 20% in China, and 3% in South Korea. Although historical declines in SMMF area have been documented, no significant changes were detected over the past 20 years. In 2021, SMMFs are highly fragmented ecosystems, primarily associated with protected areas. Conclusions: We developed a high-accuracy (0.97+-0.03) map of mixed forests using remote sensing techniques. This map facilitates the identification of valuable temperate forest regions and enhances understanding of current forest distribution. Our map is essential for planning restoration and conservation efforts for these critical ecosystems.