By: Gabriel Mukobi, Hannah Erlebach, Niklas Lauffer, Lewis Hammond, Alan Chan, Jesse Clifton
The growing capabilities and increasingly widespread deployment of AI systems necessitate robust benchmarks for measuring their cooperative capabilities. Unfortunately, most multi-agent benchmarks are either zero-sum or purely cooperative, providing limited opportunities for such measurements. We introduce a general-sum variant of the zero-sum board game Diplomacy -- called Welfare Diplomacy -- in which players must balance investing in mil... more
The growing capabilities and increasingly widespread deployment of AI systems necessitate robust benchmarks for measuring their cooperative capabilities. Unfortunately, most multi-agent benchmarks are either zero-sum or purely cooperative, providing limited opportunities for such measurements. We introduce a general-sum variant of the zero-sum board game Diplomacy -- called Welfare Diplomacy -- in which players must balance investing in military conquest and domestic welfare. We argue that Welfare Diplomacy facilitates both a clearer assessment of and stronger training incentives for cooperative capabilities. Our contributions are: (1) proposing the Welfare Diplomacy rules and implementing them via an open-source Diplomacy engine; (2) constructing baseline agents using zero-shot prompted language models; and (3) conducting experiments where we find that baselines using state-of-the-art models attain high social welfare but are exploitable. Our work aims to promote societal safety by aiding researchers in developing and assessing multi-agent AI systems. Code to evaluate Welfare Diplomacy and reproduce our experiments is available at https://github.com/mukobi/welfare-diplomacy. less
Multi-Value Alignment in Normative Multi-Agent System: An Evolutionary Optimisation Approach
0upvotes
By: Maha Riad, Vinicius de Carvalho, Fatemeh Golpayegani
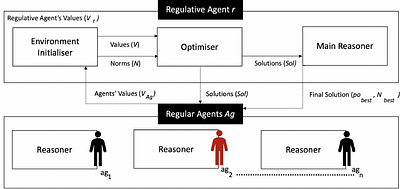
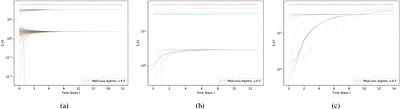
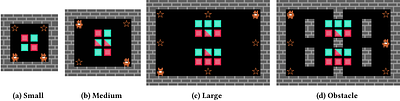
Value-alignment in normative multi-agent systems is used to promote a certain value and to ensure the consistent behaviour of agents in autonomous intelligent systems with human values. However, the current literature is limited to the incorporation of effective norms for single-value alignment with no consideration of agents' heterogeneity and the requirement of simultaneous promotion and alignment of multiple values. This research propose... more
Value-alignment in normative multi-agent systems is used to promote a certain value and to ensure the consistent behaviour of agents in autonomous intelligent systems with human values. However, the current literature is limited to the incorporation of effective norms for single-value alignment with no consideration of agents' heterogeneity and the requirement of simultaneous promotion and alignment of multiple values. This research proposes a multi-value promotion model that uses multi-objective evolutionary algorithms and decentralised reasoning to produce the optimum parametric set of norms that is aligned with multiple simultaneous values of heterogeneous agents and the system. To understand various aspects of this complex problem, several evolutionary algorithms were used to find a set of optimised norm parameters considering two toy tax scenarios with two and five values are considered. The results are analysed from different perspectives to show the impact of a selected evolutionary algorithm on the solution, and the importance of understanding the relation between values when prioritising them. less
By: Cristina Gava, Aron Vekassy, Matthew Cavorsi, Stephanie Gil, Frederik Mallmann-Trenn
We introduce the concept of community consensus in the presence of malicious agents using a well-known median-based consensus algorithm. We consider networks that have multiple well-connected regions that we term communities, characterized by specific robustness and minimum degree properties. Prior work derives conditions on properties that are necessary and sufficient for achieving global consensus in a network. This however, requires the ... more
We introduce the concept of community consensus in the presence of malicious agents using a well-known median-based consensus algorithm. We consider networks that have multiple well-connected regions that we term communities, characterized by specific robustness and minimum degree properties. Prior work derives conditions on properties that are necessary and sufficient for achieving global consensus in a network. This however, requires the minimum degree of the network graph to be proportional to the number of malicious agents in the network, which is not very practical in large networks. In this work we present a natural generalization of this previous result. We characterize cases when although global consensus is not reached, some subsets of agents $V_i$ will still converge to the same values $\mathcal{M}_i$ among themselves. We define more relaxed requirements for this new type of consensus to be reached in terms of the number $k$ of edges connecting an agent in a community to agents external to the community, and the number of malicious agents in each community. less
By: Yuxin Chen, Chen Tang, Ran Tian, Chenran Li, Jinning Li, Masayoshi Tomizuka, Wei Zhan
Generalization poses a significant challenge in Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL). The extent to which an agent is influenced by unseen co-players depends on the agent's policy and the specific scenario. A quantitative examination of this relationship sheds light on effectively training agents for diverse scenarios. In this study, we present the Level of Influence (LoI), a metric quantifying the interaction intensity among agents wi... more
Generalization poses a significant challenge in Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL). The extent to which an agent is influenced by unseen co-players depends on the agent's policy and the specific scenario. A quantitative examination of this relationship sheds light on effectively training agents for diverse scenarios. In this study, we present the Level of Influence (LoI), a metric quantifying the interaction intensity among agents within a given scenario and environment. We observe that, generally, a more diverse set of co-play agents during training enhances the generalization performance of the ego agent; however, this improvement varies across distinct scenarios and environments. LoI proves effective in predicting these improvement disparities within specific scenarios. Furthermore, we introduce a LoI-guided resource allocation method tailored to train a set of policies for diverse scenarios under a constrained budget. Our results demonstrate that strategic resource allocation based on LoI can achieve higher performance than uniform allocation under the same computation budget. less
By: Bin Zhang, Hui Zhi, Jose Guadalupe Romero, David Navarro-Alarcon
In this paper, we propose a novel formation controller for nonholonomic agents to form general parametric curves. First, we derive a unified parametric representation for both open and closed curves. Then, a leader-follower formation controller is designed to form the parametric curves. We consider directed communications and constant input disturbances rejection in the controller design. Rigorous Lyapunov-based stability analysis proves th... more
In this paper, we propose a novel formation controller for nonholonomic agents to form general parametric curves. First, we derive a unified parametric representation for both open and closed curves. Then, a leader-follower formation controller is designed to form the parametric curves. We consider directed communications and constant input disturbances rejection in the controller design. Rigorous Lyapunov-based stability analysis proves the asymptotic stability of the proposed controller. Detailed numerical simulations and experimental studies are conducted to verify the performance of the proposed method. less
Ride Acceptance Behaviour Investigation of Ride-sourcing Drivers Through Agent-based Simulation
0upvotes
By: Farnoud Ghasemi, Peyman Ashkrof, Rafal Kucharski
Ride-sourcing platforms such as Uber and Lyft offer drivers (i.e., platform suppliers) considerable freedom of choice in multiple aspects. At the operational level, drivers can freely accept or decline trip requests that can significantly impact system performance in terms of travellers' waiting time, drivers' idle time and income. Despite the extensive research into the supply-side operations, the behavioural aspects, particularly drivers'... more
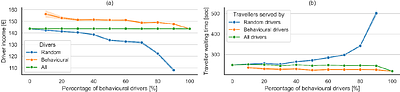
Ride-sourcing platforms such as Uber and Lyft offer drivers (i.e., platform suppliers) considerable freedom of choice in multiple aspects. At the operational level, drivers can freely accept or decline trip requests that can significantly impact system performance in terms of travellers' waiting time, drivers' idle time and income. Despite the extensive research into the supply-side operations, the behavioural aspects, particularly drivers' ride acceptance behaviour remains so far largely unknown. To this end, we reproduce the dynamics of a two-sided mobility platform on the road network of Delft using an agent-based simulator. Then, we implement a ride acceptance decision model enabling drivers to apply their acceptance strategies. Our findings reveal that drivers who follow the decision model, on average, earn higher income compared to drivers who randomly accept trip requests. The overall income equality between drivers with the acceptance decision is higher and travellers experience lower waiting time in this setting. less
By: Davide Basile, Claudio Di Ciccio, Valerio Goretti, Sabrina Kirrane
Decentralization initiatives like Solid enable data owners to control who has access to their data and to stimulate innovation by creating both application and data markets. Once data owners share their data with others, though, it is no longer possible for them to control how their data are used. To address this issue, we propose a usage control architecture to monitor compliance with usage control policies. To this end, our solution relie... more
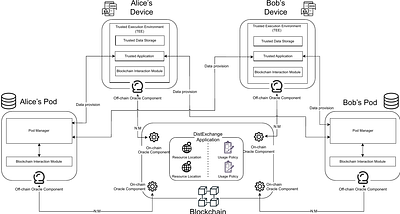
Decentralization initiatives like Solid enable data owners to control who has access to their data and to stimulate innovation by creating both application and data markets. Once data owners share their data with others, though, it is no longer possible for them to control how their data are used. To address this issue, we propose a usage control architecture to monitor compliance with usage control policies. To this end, our solution relies on blockchain and trusted execution environments. We demonstrate the potential of the architecture by describing the various workflows needed to realize a motivating use case scenario for data markets. Additionally, we discuss the merits of the approach from privacy, security, integrateability, and affordability perspectives. less
By: Kazumi Kasaura
We propose an efficient framework using the Dehornoy order for homotopy-aware multi-agent path planning in the plane. We developed a method to generate homotopically distinct solutions of multi-agent path planning problem in the plane by combining our framework with revised prioritized planning and proved its completeness under specific assumptions. Experimentally, we demonstrated that the runtime of our method grows approximately quintical... more
We propose an efficient framework using the Dehornoy order for homotopy-aware multi-agent path planning in the plane. We developed a method to generate homotopically distinct solutions of multi-agent path planning problem in the plane by combining our framework with revised prioritized planning and proved its completeness under specific assumptions. Experimentally, we demonstrated that the runtime of our method grows approximately quintically with the number of agents. We also confirmed the usefulness of homotopy-awareness by showing experimentally that generation of homotopically distinct solutions by our method contributes to planning low-cost trajectories for a swarm of agents. less
By: Kinal Mehta, Anuj Mahajan, Pawan Kumar
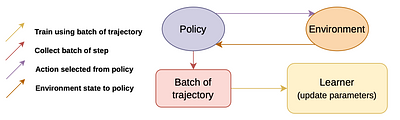
Recent advances in Reinforcement Learning (RL) have led to many exciting
applications. These advancements have been driven by improvements in both
algorithms and engineering, which have resulted in faster training of RL
agents. We present marl-jax, a multi-agent reinforcement learning software
package for training and evaluating social generalization of the agents. The
package is designed for training a population of agents in multi-agent
e... more
Recent advances in Reinforcement Learning (RL) have led to many exciting
applications. These advancements have been driven by improvements in both
algorithms and engineering, which have resulted in faster training of RL
agents. We present marl-jax, a multi-agent reinforcement learning software
package for training and evaluating social generalization of the agents. The
package is designed for training a population of agents in multi-agent
environments and evaluating their ability to generalize to diverse background
agents. It is built on top of DeepMind's JAX ecosystem~\cite{deepmind2020jax}
and leverages the RL ecosystem developed by DeepMind. Our framework marl-jax is
capable of working in cooperative and competitive, simultaneous-acting
environments with multiple agents. The package offers an intuitive and
user-friendly command-line interface for training a population and evaluating
its generalization capabilities. In conclusion, marl-jax provides a valuable
resource for researchers interested in exploring social generalization in the
context of MARL. The open-source code for marl-jax is available at:
\href{https://github.com/kinalmehta/marl-jax}{https://github.com/kinalmehta/marl-jax}
less