Persistent Anhedonia After Intermittent Long-Access Nicotine Self-Administration in Rats
Persistent Anhedonia After Intermittent Long-Access Nicotine Self-Administration in Rats
Chellian, R.; Behnood-Rod, A.; Bruijnzeel, A.
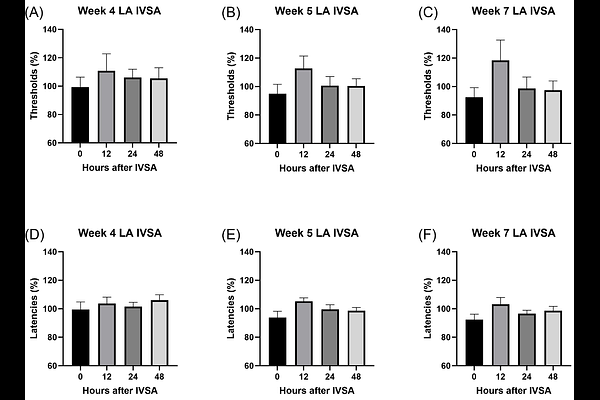
AbstractTobacco use disorder is a chronic condition characterized by compulsive nicotine use and withdrawal symptoms after smoking cessation. Smoking is the leading preventable cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Smoking cessation leads to anhedonia, which is an inability to experience pleasure from previously enjoyed activities and is caused by dysregulation of the brain's reward and stress systems. It is also a key withdrawal symptom that contributes to relapse to smoking after a period of abstinence. To better understand the development of anhedonia, we investigated its onset and time course in rats that self-administered nicotine. Rats were implanted with intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) electrodes to assess reward function and intravenous catheters for nicotine self-administration. Elevations in ICSS brain reward thresholds reflect decreased sensitivity to rewarding electrical stimuli, indicating anhedonia. The rats self-administered 0.06 mg/kg of nicotine intermittently, three days per week, for seven weeks. Brain reward thresholds were determined once a week 24 h after nicotine self-administration during weeks 1 to 3, and at 12, 24, and 48 h during weeks 4, 5, and 7. Elevations in brain reward thresholds were not observed during the first four weeks of nicotine self-administration. However, the brain reward thresholds were elevated in both weeks 5 and 7 at least 12 h after nicotine self-administration, indicating that anhedonia emerges gradually and then persists. As withdrawal severity gradually increases, smoking cessation may become more challenging. Therefore, behavioral or pharmacological interventions soon after smoking initiation are critical to prevent the development of a tobacco use disorder.