PrPC-induced signaling in human neurons activates phospholipase Cγ1 and an Arc/Arg3.1 response
PrPC-induced signaling in human neurons activates phospholipase Cγ1 and an Arc/Arg3.1 response
Ojeda-Juarez, D.; Funk, G.; Richards, E.; Rajic, A. J.; McClatchy, D. B.; Soldau, K.; Chen, X.; Yates, J. R.; Gonias, S. L.; Sigurdson, C. J.
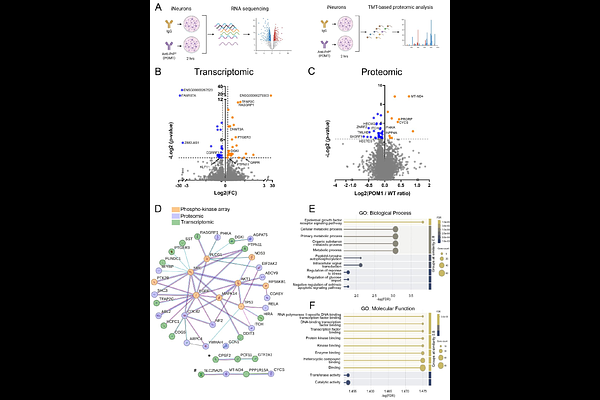
AbstractSynaptic dysfunction and loss correlate with cognitive decline in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer disease (AD) and prion disease. Neuronal hyperexcitability occurs in the early stages of AD and experimental prion disease, prior to the onset of dementia, yet the underlying drivers are unclear. Here we identify an increase in the immediate early gene, Arc/Arg3.1, in the human prion disease-affected frontal cortex, suggestive of neuronal hyperactivity. To investigate early signaling events initiated by prion aggregates (PrPSc) in human neurons, we stimulated PrPC in human iPSC-derived excitatory neurons (iNs) with a known PrPSc-mimetic antibody (POM1), which recapitulated the Arc/Arg3.1 response within two hours. Proteomics, RNAseq, and a phosphokinase array in iNs revealed alterations in the EGF receptor and increased phosphorylated phospholipase C (PLC)-{gamma}1 (Y783), which was also observed in the cerebral cortex of prion-infected mice. Thus, PrPC ligands can induce a PLC-{gamma}1 intracellular signaling cascade together with an Arc response, mimicking a neuronal activity response.